Using water pump by ESP32 card
Tutorial plan
1- How command water pump by ESP32 card ?
2- Components Needed
3- Circuit Setup
4- Programming ESP32 with Micropython
How command pump by ESP32 board ?
To control a water pump with an ESP32, a relay module, and a push button, you’ll create a circuit and code setup that toggles the pump on and off with each press of the button. The ESP32 microcontroller will read the button input and use the relay to switch the water pump's power.
System Overview
1- ESP32: This microcontroller will monitor the push button and control the relay. The ESP32 will toggle the relay, which in turn controls the power to the pump.
2- Relay Module: This acts as a switch for the pump. Since the ESP32 operates on low voltage, it cannot directly drive the pump. The relay safely isolates the ESP32 from the higher power required by the pump.
3- Push Button: A simple push button acts as a manual control to toggle the pump on or off. Each button press changes the state of the relay and, consequently, the water pump.
Components Needed
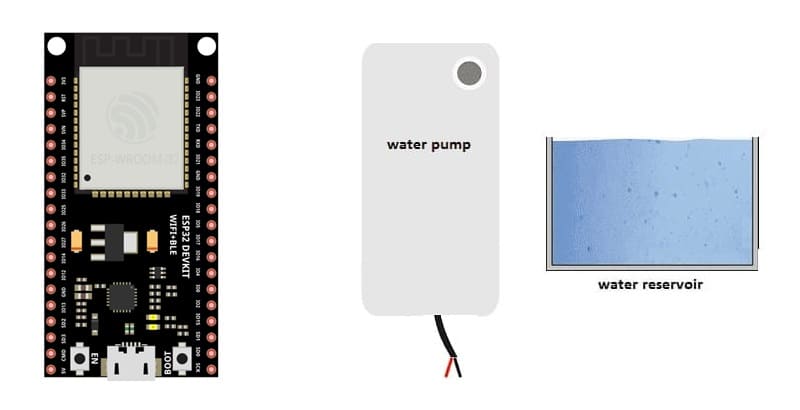
1- ESP32 board

The ESP32 board is a microcontroller board that reads button inputs and controls the relay.
2- 12V Water pump

A 12V water pump is an excellent choice for small projects due to its manageable power requirements and compatibility with many microcontrollers like ESP32.
3- Relay Module (for controlling the water pump with ESP32):
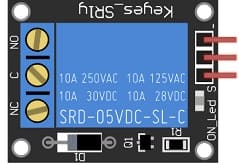
A relay module allows the ESP32 to control a high-power device like a water pump by isolating the pump's high voltage from the ESP32’s low voltage. When the ESP32 sends a signal, the relay switches on, allowing current to flow through the pump and activate it.
4- Push button:

The push button is a simple input device that sends a signal to the ESP32 when pressed. The ESP32 detects button presses to toggle the relay.
4- Power supply for the water pump (matching the pump's requirements)
You’ll need a 9V power supply that provides enough current for the pump to operate effectively.
5- Jumper Wires

Jumper wires will be used to make connections between the components.
6- Breadboard:

A breadboard can be used to create a temporary circuit for testing and prototyping.
Circuit Setup
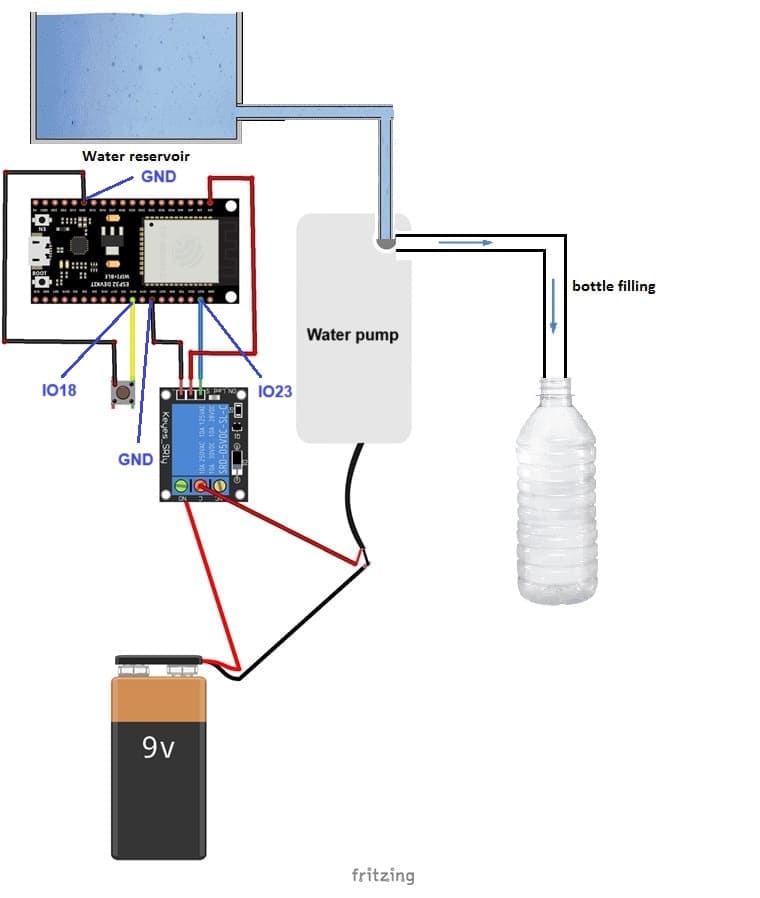
Relay Configuration:
1- Connect the relay module’s IN pin to one of the ESP32’s GPIO pins (e.g., GPIO 23).
2- Connect the VCC and GND of the relay module to the ESP32’s 3.3V (or 5V, depending on the relay) and GND pins.
3- Connect the water pump to the NO (Normally Open) of the relay.
4- Connect the water pump’s power supply to the COM terminal and the pump’s positive terminal. The pump’s negative terminal should connect directly to the power supply’s ground.
Button Connections:
1- Connect one side of the button to GPIO 18 (or any other free GPIO pin) on the ESP32.
2- Connect the other side of the button to GND on the ESP32.
Programming the ESP32 with Micropython
Here’s a simple code that toggles the pump on or off each time you press the button.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
import machine from machine import Pin buttonPin = machine.Pin(18, machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP) pumpPin=Pin(23,Pin.OUT) # set pin D23 of ESP32 to output mode while True: if not buttonPin.value(): # We press the button pumpPin.value(1) # the water pump fills the bottle else: # we release the button pumpPin.value(0) # the water pump stops |
Explanation
- buttonPin is set to read the state of the push button.
- Each time the button is pressed, the pumpState variable is toggled between true (on) and false (off).
- pumpPin.value switches the relay (and thus the pump) based on the pumpState.

























