Turn on three LEDs using radio communication between two Micro:bit boards
Tutorial plan
1- Introduction to the Micro:bit Board Radio Module
2- Controlling three LEDs by radio communication from the Micro:bit board
3- The components needed to control three LEDs by Micro:bit
4- Mounting the Micro:bit board with an three LEDs
Introduction to the Micro:bit Board Radio Module
The BBC micro:bit is a pocket-sized computer board designed for educational purposes. It has a built-in radio module that allows micro:bit boards to communicate with each other wirelessly. The radio module on the micro:bit uses Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology, which enables short-range communication between devices.
The radio module on the micro:bit board allows for wireless communication and data transfer. It operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band and supports a range of up to 30 meters (or about 100 feet) in an open space environment. The micro:bit radio module can be used for various applications, such as creating interactive games, sending messages between devices, or building remote-controlled projects.
To use the radio module on the micro:bit, you can program it using the micro:bit's programming environments, such as the Microsoft MakeCode editor or the MicroPython programming language. These environments provide blocks or functions specifically designed to control the radio module and enable communication between micro:bit boards.
By utilizing the radio module, you can establish a communication link between multiple micro:bit boards, allowing them to exchange data, coordinate actions, or create collaborative projects. It's a powerful feature that adds interactivity and connectivity to your micro:bit projects.
Controlling an three LEDs by radio communication from the Micro:bit board
To control an three LEDs using radio communication from one micro:bit board to another, you'll need three micro:bit boards—one acting as a transmitter and the other as a receiver. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to accomplish this:
Transmitter (Micro:bit A):
1- Connect three LEDs to micro:bit's GPIO pins (for example, P0 for red LED, P1 for green LED and P2 for yellow LED). Ensure to use a current-limiting resistor (e.g., 220-470 ohms) in series with the LED.
2- Open the Microsoft MakeCode editor.
3- Write the following code to send radio messages:
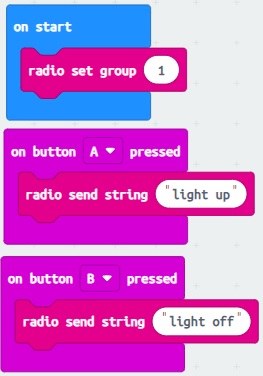
4- Download the code to the micro:bit (A) and disconnect it from the computer.
Receiver (Micro:bit B):
1- Connect another micro:bit board to your computer and open the programming environment.
2- Write the following code to receive radio messages and control the three LEDs:
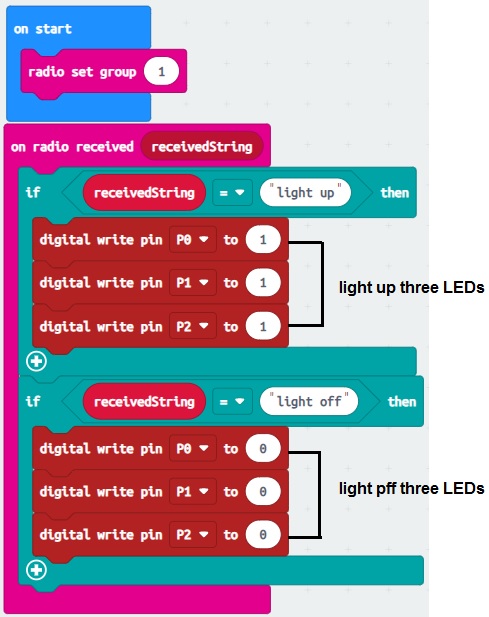
3- Download the code to the micro:bit (B) and disconnect it from the computer.
Now, whenever you press button A on the transmitter micro:bit (A), it will turn on the three LEDs connected to P0 micro:bit (B).
whenever you press button B on the transmitter micro:bit (A), it will turn off the three LEDs connected to P0 micro:bit (B).
The components needed to control three LED by Micro:bit
To control an LED using a Micro:bit, you will need the following components:
Two Micro:bit board
The Micro:bit board is a small, programmable development board designed for educational purposes and beginner-friendly programming. It was created as a collaboration between several organizations, including the BBC, in order to promote computer science education and coding skills among young learners.
With the Micro:bit board, users can create a wide range of projects and interactive applications. They can write programs to control the LEDs, read sensor data, respond to button presses, and communicate with other devices using Bluetooth. The versatility of the board allows for creative exploration and learning in areas such as robotics, Internet of Things (IoT), and wearable technology.
The Micro:bit has gained popularity in schools, coding clubs, and maker communities around the world as an affordable and engaging tool for teaching coding concepts and electronics. Its compact size and user-friendly interface make it an excellent choice for beginners, while its capabilities and extensibility provide room for more advanced projects as well. 
The GPIO expansion card for the Micro:bit card
The GPIO expansion board for the Micro:bit board expands the capabilities of the Micro:bit board by adding more input/output (GPIO) pins and additional functionality. 
LEDs:
You will need three LEDs of your choice. These can be regular LEDs or RGB LEDs, depending on your project requirements.
Resistors:
LEDs require current-limiting resistors to prevent them from burning out. The value of the resistor depends on the forward voltage and current rating of the LEDs. A typical value for a standard LED is around 220-470 ohms.
Jumper wires
You will need jumper wires to connect the Micro:bit to the LED and the current-limiting resistor. Make sure you choose the appropriate type of jumper wires (e.g., male-to-male, male-to-female, or female-to-female) based on your specific setup. 
Test plate
The breadboard is a common tool used in robotics and electronics to create circuit prototypes and temporary connections. It makes it easy to test and connect electronic components together without having to solder the connections.
Once you have gathered these components, you can properly connect them and program the Micro:bit board to control the LED as needed. Be sure to follow good connection and safety practices when handling electronic components. 
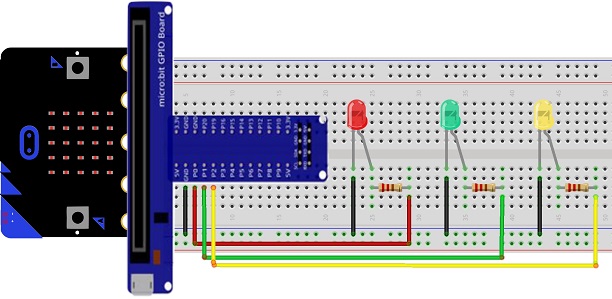
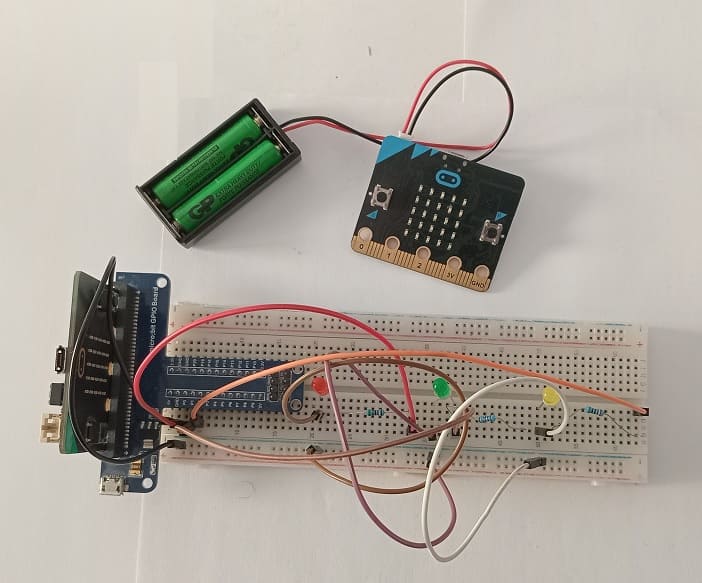
Mounting the Micro:bit board with three LEDs
Mounting three LEDs on a Micro:bit board is a common project that can be accomplished with a few simple steps. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you:
1- Place your Micro:bit board on a flat surface.
2- Take three LEDs of your choice and identify their legs. LEDs have a longer leg called the anode (+) and a shorter leg called the cathode (-).
3- Connect the cathode of the first LED to GND on the Micro:bit board. Use a jumper wire to make this connection.
4- Connect the anode of the first LED to the resistor's leg. The other leg of the resistor should be connected to the pin P0 on the Micro:bit board.
5- Repeat steps 3 and 4 for the other two LEDs, connecting them to pins P1 and P2 on the Micro:bit board.
6- Make sure the resistors are connected to the cathodes of the LEDs and the other leg of each resistor is connected to the GND pin.
7- If you're using a breadboard, you can connect the jumper wires to the appropriate pins on the Micro:bit board and insert the LED legs and resistors into the breadboard for a neat and organized setup.