The LEDs

LED definition
LED stands for "Light Emitting Diode." It is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current is passed through it. LEDs are used in a wide range of applications, including lighting, displays, and indicators. Compared to traditional light sources such as incandescent bulbs and fluorescent lamps, LEDs are more energy-efficient, have a longer lifespan, and are more environmentally friendly because they do not contain hazardous materials such as mercury. LEDs are also more durable and can withstand shock, vibration, and temperature changes better than other types of lighting.
What is an LED made of ?
An LED, or Light Emitting Diode, is made up of several layers of semiconductor materials. The most common semiconductor materials used to make LEDs are gallium arsenide (GaAs), gallium phosphide (GaP), and gallium nitride (GaN). These semiconductor materials are doped with impurities to create a p-n junction, which is the basic building block of an LED.
The p-n junction is formed by combining a p-type semiconductor, which has an excess of positively charged "holes" in its crystal lattice, with an n-type semiconductor, which has an excess of negatively charged "electrons". When a voltage is applied across the p-n junction, the electrons and holes combine at the junction, releasing energy in the form of photons, which are the particles of light.
The color of the light emitted by an LED depends on the type of semiconductor material used and the doping impurities. For example, LEDs made of GaAs emit infrared light, while LEDs made of GaP emit red or green light, and LEDs made of GaN emit blue or white light. The size and shape of the semiconductor layers also play a role in determining the properties of an LED, such as its brightness and efficiency.
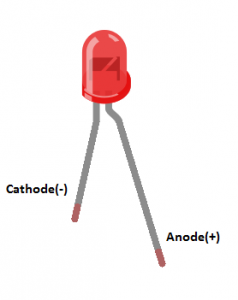
In an LED, the cathode and anode are the two electrodes or terminals that allow current to flow through the semiconductor layers to produce light.
The cathode is the negative electrode of the LED, and it is usually marked with a shorter lead or a flat side on the LED's housing. The cathode is connected to the n-type semiconductor layer of the LED, which has an excess of free electrons.
The anode is the positive electrode of the LED, and it is usually marked with a longer lead or a rounded side on the LED's housing. The anode is connected to the p-type semiconductor layer of the LED, which has an excess of positively charged "holes".
When a voltage is applied across the cathode and anode of the LED, electrons and holes are injected into the p-n junction, where they recombine and release energy in the form of photons, which are the particles of light. The color and intensity of the light emitted by the LED depend on the materials used to make the semiconductor layers and the current flowing through the device.
LEDs and robotics
LEDs are commonly used in robotics for various applications such as visual feedback, illumination, and status indicators. Here are a few examples of how LEDs can be used in robotics:
Visual feedback: LEDs can be used to provide visual feedback to the user or operator of the robot. For example, LEDs can be used to indicate the status of the robot, such as whether it is on or off, whether it is in a particular mode, or whether it has encountered an error.
Illumination: LEDs can be used to provide illumination for the robot's camera or sensors. For example, if the robot is operating in low light conditions, it may use LEDs to provide additional light to its sensors to improve its ability to perceive its surroundings.
Status indicators: LEDs can be used to provide status indicators for the robot's various components. For example, LEDs can be used to indicate the battery level, the status of the motor drivers, or the status of the sensors.
Decoration: LEDs can also be used for decorative purposes on robots. For example, LEDs can be used to create patterns or designs on the robot's exterior to make it more visually appealing.
LEDs and microcontrollers
LEDs are often used in conjunction with microcontrollers to create simple and complex electronic systems. Microcontrollers are small computers that can be programmed to control the behavior of electronic devices, including LEDs. Here are some ways in which LEDs can be used with microcontrollers:
Controlling LED brightness: Microcontrollers can be used to control the brightness of LEDs by varying the amount of current supplied to the LED. By pulsing the current to the LED at high frequencies, microcontrollers can create the illusion of a dimmer or brighter light.
Creating LED animations: Microcontrollers can be used to program complex LED animations by turning individual LEDs on and off in specific patterns. For example, a microcontroller can be programmed to make an LED flash, pulse, or change colors in response to certain events or inputs.
Building LED matrices: Microcontrollers can be used to drive large arrays of LEDs, known as LED matrices. By using specialized software and hardware, microcontrollers can control the behavior of individual LEDs in the matrix to create scrolling messages, images, or animations.
Developing LED displays: Microcontrollers can be used to control the behavior of LED displays, such as 7-segment displays or dot matrix displays. By sending specific signals to the LEDs, microcontrollers can display numerical values, letters, and symbols on the display.