Obstacle detection system based on HC-SR04 sensor and ESP32
Introduction
1- Working principle of obstacle detection system based on HC-SR04 and ESP32
2- Necessary system components
3- Obstacle detection system wiring diagram
4- Programming the ESP32 board with Micropython
Introduction
An obstacle detection system is a technology designed to identify and alert users or autonomous systems about obstacles or hazards in their environment. These systems are commonly used in various applications, including robotics, autonomous vehicles, drones, industrial automation, and assistive technologies. The primary goal is to enhance safety and prevent collisions by providing real-time information about the presence of obstacles.
Here are some key components and technologies often employed in obstacle detection systems:
Sensors:
Ultrasonic Sensors: These sensors use ultrasonic waves to measure the distance between the sensor and an object. They are commonly used for short-range obstacle detection.
Infrared Sensors: Infrared sensors can detect obstacles by emitting and receiving infrared radiation. They are suitable for both short and medium-range applications.
Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging): Lidar systems use laser beams to measure distances and create a detailed 3D map of the surroundings. Lidar is often used in autonomous vehicles and robotics for accurate obstacle detection.
Radar (Radio Detection and Ranging): Radar systems use radio waves to detect the presence and location of objects. They are effective for long-range obstacle detection and are commonly used in automotive applications.
Computer Vision:
Cameras: Image sensors and cameras can be used to capture visual information, and computer vision algorithms can analyze the images to identify obstacles. This method is widely used in various applications, including surveillance systems and autonomous vehicles.
Depth Sensors: Depth-sensing cameras or sensors, such as time-of-flight (ToF) cameras, provide information about the distance to objects, aiding in obstacle detection.
Data Processing and Fusion:
The raw data from sensors need to be processed and fused to create a comprehensive understanding of the environment. This involves filtering, combining, and interpreting data to accurately identify obstacles.
Algorithms:
Various algorithms, including machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques, can be employed to improve the accuracy and reliability of obstacle detection. These algorithms can adapt to different environments and learn from experience.
Alert Systems:
Once an obstacle is detected, the system needs to communicate this information to the user or the controlling system. This could be through visual alerts, audible alarms, or other communication methods.
Integration with Control Systems:
In many applications, obstacle detection systems are integrated with control systems to enable automated responses, such as slowing down a vehicle or stopping a robot when an obstacle is detected.
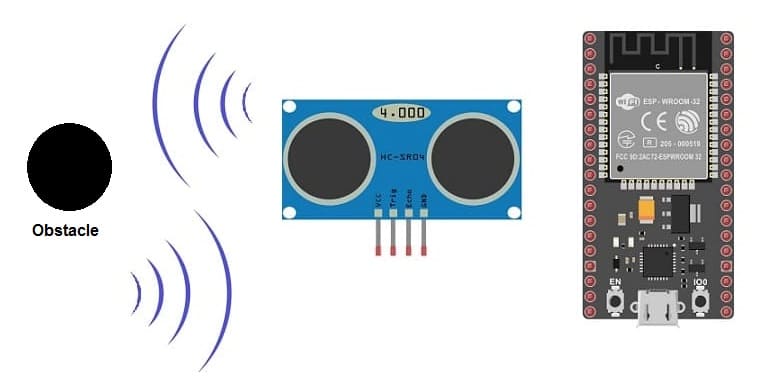
Working principle of obstacle detection system based on HC-SR04 and ESP32
An obstacle detection system based on HC-SR04, a buzzer, an LED, and an ESP32 microcontroller can provide both visual and audible feedback when an obstacle is detected. Here's a simple overview of the working principle:
Components:
HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor:
Transmitter: Emits ultrasonic waves.
Receiver: Detects reflected waves.
ESP32 Microcontroller:
Processor: Executes the program logic.
GPIO Pins: Used to connect to the HC-SR04 sensor, LED, and buzzer.
Buzzer:
An electronic buzzer that produces sound when activated.
LED:
A light-emitting diode that provides a visual indicator.
Working Principle:
Trigger and Echo Signals: The HC-SR04 sends a trigger signal and measures the time it takes for the ultrasonic waves to travel to an obstacle and back (echo signal).
Ultrasonic Pulse Generation: The ESP32 generates a short pulse (10 microseconds) to the trigger pin of the HC-SR04, initiating the ultrasonic wave emission.
Reflection from Obstacle: If there's an obstacle in the path, ultrasonic waves are reflected back towards the sensor.
Echo Signal Detection: The HC-SR04 detects the reflected waves and generates an echo signal, and the ESP32 measures the time it takes for the echo signal to return.
Distance Calculation: Using the speed of sound in air, the ESP32 calculates the distance using the formula: Distance = (Time * Speed of Sound) / 2.
Threshold Comparison: The calculated distance is compared to a predefined threshold distance. If the distance is less than the threshold, it indicates the presence of an obstacle.
Activation of Buzzer and LED: If an obstacle is detected, the ESP32 activates the buzzer to produce an audible alert and turns on the LED to provide a visual indicator.
Continuous Monitoring: The system continuously monitors for obstacles, repeating the process to provide real-time feedback. Adjustments can be made based on changing conditions.
Necessary system components
ESP32 board:
The ESP32 is a powerful microcontroller developed by Espressif Systems. It's renowned for its integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, making it a popular choice for various IoT (Internet of Things) applications.
HC-SR04 ultrasonic Sensor

The HC-SR04 is an ultrasonic distance measuring sensor module.
LED
![]()
In an obstacle detection system, an LED (Light Emitting Diode) can be used as a visual indicator to provide feedback about the detection status. The LED can be programmed to turn on or off based on whether an obstacle is detected within a certain range.
Resistance (220 ohm)
![]()
The resistance needed for an LED (Light Emitting Diode) in a circuit is determined by Ohm's Law, which states that the resistance (R) is equal to the voltage (V) divided by the current (I).
Jumper Wires:

For making temporary connections and wiring between components.
Breadboard:

A breadboard is a useful tool for creating temporary electronic circuits. It allows you to connect components without soldering.
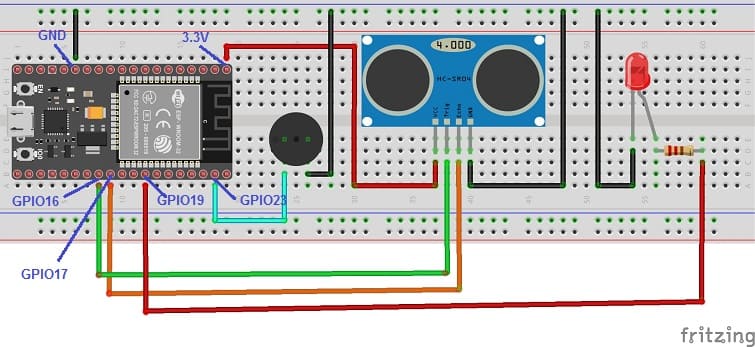
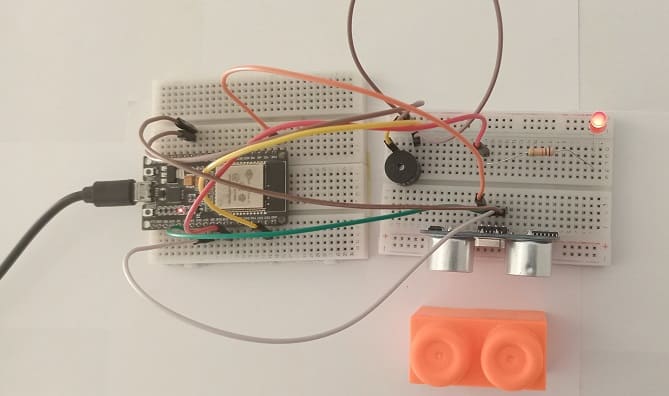
Obstacle detection system wiring diagram
Attaching the HC-SR04 sensor :
- Connect the VCC(+) pin of the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor to the 3.3V pin on the ESP32 board.
- Connect the Trig pin of the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor to GPIO16 pin on the ESP32 board.
- Connect the Echo pin of the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor to GPIO17 pin on the ESP32 board.
- Connect the GND(-) pin of the DHT22 sensor to any ground (GND) pin on the ESP32 board.
Attaching the buzzer :
- Connect the (+) terminal of buzzer to GPIO23 pin on the ESP32 board.
- Connect the (-) terminal of buzzer to GND pin on the ESP32 board.
Attaching the red LED :
- Connect the negative terminal (cathode) of each LED to the ground (GND) of the ESP32 board.
- Connect a resistor between the GPIO19 pin and the positive terminal (anode) of the LED
Programming the ESP32 board with Micropython
To program an obstacle detection system using HC-SR04, a buzzer, an LED, and an ESP32 with Micropython, you'll need to follow these steps.
1- Make sure you have Micropython installed on your ESP32 board.
2- Flash your ESP32 with MicroPython using this file esp32-20210902-v1.17.bin.
3- import this library : hc-sr04 for HC-SR04 sensor
4- Create a new Python script and write the following code :
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
import machine from machine import Pin from hcsr04 import HCSR04 import time # Configure GPIO pins sensor = HCSR04(trigger_pin=16,echo_pin=17,echo_timeout_us=1000000) redled_pin=Pin(19, Pin.OUT) buzzer_pin=Pin(23, Pin.OUT) while True: # Calculate distance distance = sensor.distance_cm() print('distance= ',distance,' cm') # Check if obstacle is detected if (distance<4): # Activate buzzer and LED redled_pin.value(1) buzzer_pin.value(1) else: # Deactivate buzzer and LED redled_pin.value(0) buzzer_pin.value(0) time.sleep_ms(100) |