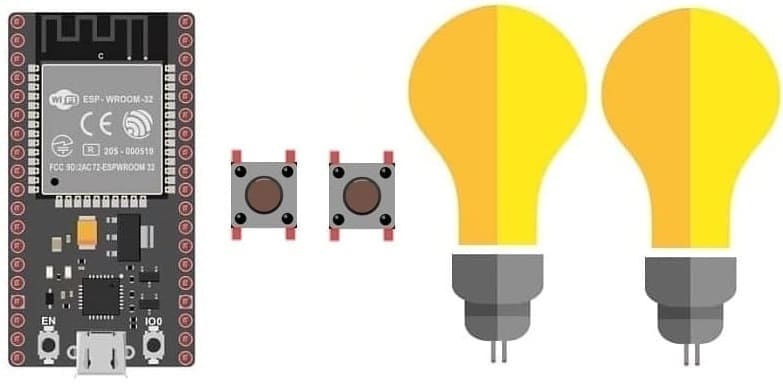
Light up two lamps connected to ESP32 board using the push buttons
Tutorial plan
1- Role of the push button in robotics
2- The components necessary to control two lamps by the push buttons and the ESP32 board
3- Mounting the ESP32 board with two lamps, two relays and two push buttons
4- Micropython programming of the ESP32 card to turn on two lamps using the push buttons
Role of the push button in robotics
Push buttons can play a significant role in robotics by serving as a means of human interaction and control in various ways:
Start/Stop Control: Push buttons are often used to start and stop robotic systems. For example, a start button can initiate the robot's operation, and a stop button can halt it in case of an emergency or to end a task.
Emergency Stop (E-Stop): Emergency stop buttons are critical safety features in robotics. They provide an immediate and easily accessible way to shut down the robot in case of a malfunction or a hazardous situation. This is crucial for ensuring the safety of both the robot and the people working around it.
Mode Selection: In more complex robotic systems, push buttons can be used to select different operational modes, such as autonomous mode, manual control mode, or specific task modes. Users can switch between these modes using buttons.
User Interface: Push buttons can be used to provide a simple user interface for users to interact with the robot. They can trigger specific actions or functions, like moving an arm, activating a gripper, or changing the robot's behavior.
Teaching and Programming: Push buttons can be used in a teaching or programming mode, where operators can manually move robot arms or other components to demonstrate desired motions or trajectories. This information can be recorded and later reproduced by the robot.
Limit or Home Switches: Push buttons can be used as limit switches or home switches in robotics. They help the robot establish reference points or boundaries for its movement, ensuring accuracy and safety.
Calibration and Configuration: Push buttons can be used for calibrating sensors, configuring parameters, or setting up the robot's initial conditions. They can be part of a setup process to ensure that the robot operates as intended.
Reset or Clear Function: Push buttons can be used to reset the robot's state, clear error conditions, or restart specific tasks. They can help recover from unexpected situations.
User Feedback: Some push buttons may include indicator lights or displays to provide feedback to the user, such as the current mode, status, or system health.
Push buttons, when combined with microcontrollers and control systems, offer a convenient way for humans to interact with and control robots, whether in industrial automation, research, or various other applications. Their design and functionality can vary based on the specific needs of the robotic system and the safety requirements associated with it.
The components necessary to control two lamp by the push buttons and the ESP32 board
To control two lamps using the ESP32 board, you will need the following components:
ESP32 Board:
The ESP32 is a microcontroller board that features built-in WiFi and Bluetooth capabilities. It can be programmed and used to control the two lamps.
Push button:

A push button, also known as a momentary switch or tactile switch, is a simple yet commonly used electromechanical component in electronics. It is designed to make or break an electrical connection temporarily when pressed or released.
Two Relays Modules:
You'll need a relay module that is compatible with the ESP32 card and can switch the high-voltage lamp. Ensure it's rated for the voltage and current required for your lamp.
Two Lamps (220V):

The lamps you want to control, which is rated for 220V. Ensure it's in working condition and safe to use.
Power Supply for the Lamp:

You'll need a power source for the lamp, typically a 220V AC power supply.
Wiring:

Various wires and cables for connecting the components in your circuit.
Breadboard:

A breadboard is a prototyping board that allows you to build circuits without soldering. It provides a convenient way to connect the components together.
Jumper Wires:

You'll need jumper wires to make connections between the ESP32 card, lamp, relay, push button and breadboard. Ensure you have male-to-male jumper wires or a mix of male-to-male and male-to-female wires, depending on your specific needs.
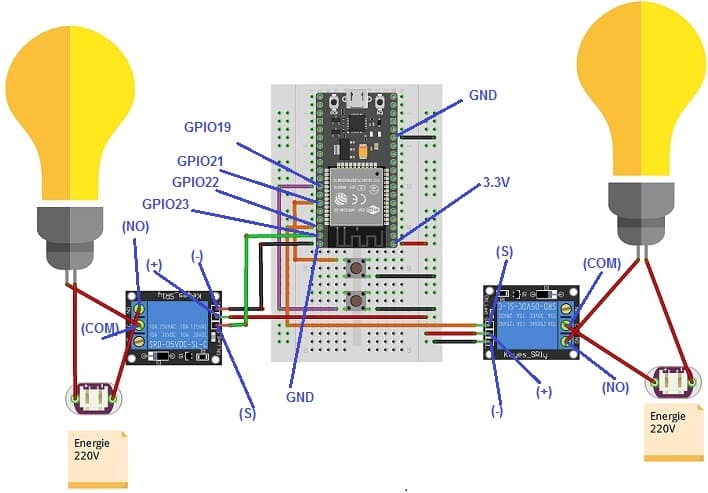
Mounting the ESP32 card with two lamps, two relays and two push buttons
To control two lamps using a ESP32 board, you will need to use two relays modules to safely interface the low-voltage ESP32 card with the high-voltage lamp.
1- Connect the first push button to the ESP32 board:
- Connect one leg of the push button to pin GPIO 21 of the ESP32 board.
- Connect another leg of the push button to pin GND of the ESP32 board.
2- Connect the first relay to the ESP32 board:
- Connect the relay's control pin (S) to pin 23 of ESP32 board.
- Connect the pin (+) of relay to pin 3.3V of ESP32 board.
- Connect the relay's ground pin (GND) to the ESP32's GND.
3- Connect the first lamp and the power supply to the Relay:
- Connect one of the power supply's wires to the relay's common (COM) terminal.
- Connect the phase wire of the the lamp to the normally open (NO) terminal of the relay.
- Connect the neutral wire of the power supply directly to the neutral wire of the lamp.
4- Connect the second push button to the ESP32 board:
- Connect one leg of the push button to pin GPIO 19 of the ESP32 board.
- Connect another leg of the push button to pin GND of the ESP32 board.
5- Connect the second relay to the ESP32 board:
- Connect the relay's control pin (S) to pin 22 of ESP32 board.
- Connect the pin (+) of relay to pin 3.3V of ESP32 board.
- Connect the relay's ground pin (GND) to the ESP32's GND.
6- Connect the second lamp and the power supply to the Relay:
- Connect one of the lamp's wires to the relay's common (COM) terminal.
- Connect the phase wire of the power supply to the normally open (NO) terminal of the relay.
- Connect the neutral wire of the power supply directly to the neutral wire of the lamp.
Micropython programming of the ESP32 card to turn on two lamps using the push buttons
You can connect to your ESP32 board using a serial terminal (e.g., PuTTY, minicom) or use a tool like Thonny to write and execute MicroPython code.
Here's a simple example code to turn on the two lamps when the push button are pressed:
1- Import the necessary modules:
|
1 2 |
import machine from machine import Pin import time |
2- Configure the pins (GPIO) for the push button and the relays which should light the two lamps:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
lamp1_button = machine.Pin(21, machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP) lamp1_relay=Pin(23, Pin.OUT) lamp2_button = machine.Pin(19, machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP) lamp2_relay=Pin(22, Pin.OUT) |
3- Create a variable to keep the state of the relay (0 if the lamp is off and 1 if the lamp is on)
|
1 2 |
lamp1_state=0; lamp2_state=0; |
Create a loop to monitor the pushbutton status and turn the lamp on/off accordingly:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
while True: lamp1_first = lamp1_button.value() time.sleep(0.01) lamp1_second = lamp1_button.value() if lamp1_first and not lamp1_second: print('Button pressed!') if (lamp1_state==0): lamp1_relay.value(1) #turn on the first lamp lamp1_state=1 else: lamp1_relay.value(0) #turn off the first lamp lamp1_state=0; time.sleep(0.5) elif not lamp1_first and lamp1_second: print('Button released!') #led_rouge.value(0) lamp2_first = lamp2_button.value() time.sleep(0.01) lamp2_second = lamp2_button.value() if lamp2_first and not lamp2_second: print('Button pressed!') if (lamp2_state==0): lamp2_relay.value(1) #turn on the second lamp lamp2_state=1 else: lamp2_relay.value(0) #turn off the second lamp lamp2_state=0; time.sleep(0.5) elif not lamp2_first and lamp2_second: print('Button released!') |
Here is the complete program in Micropython:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
import machine from machine import Pin import time lamp1_relay=Pin(23, Pin.OUT) lamp1_button= machine.Pin(21, machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP) lamp1_state=0; lamp2_relay=Pin(22, Pin.OUT) lamp2_button = machine.Pin(19, machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP) lamp2_state=0; while True: lamp1_first = lamp1_button.value() time.sleep(0.01) lamp1_second = lamp1_button.value() if lamp1_first and not lamp1_second: print('Button pressed!') if (lamp1_state==0): lamp1_relay.value(1) lamp1_state=1 else: lamp1_relay.value(0) lamp1_state=0; time.sleep(0.5) elif not lamp1_first and lamp1_second: print('Button released!') #led_rouge.value(0) lamp2_first = lamp2_button.value() time.sleep(0.01) lamp2_second = lamp2_button.value() if lamp2_first and not lamp2_second: print('Button pressed!') if (lamp2_state==0): lamp2_relay.value(1) lamp2_state=1 else: lamp2_relay.value(0) lamp2_state=0; time.sleep(0.5) elif not lamp2_first and lamp2_second: print('Button released!') |
When the button is pressed (the state is low), the lamp lights up. If the button is pressed another time, the lamp turns off. The 0.5 second delay is used to prevent pushbutton bounce, which can cause multiple button activations with a single press.
This simple example demonstrates how to use MicroPython to control two lamps using relays and the push buttons with an ESP32 board.