Display temperature and humidity measured by DHT11 sensor connected to Arduino on SSD1306 display
Tutorial plan
1- How to use the DHT11 sensor by the Arduino UNO board ?
2- The components required to display the temperature and humidity measured by the DHT11 sensor connected to Arduino on the SSD1306 display
3- Mounting the Arduino board with the DHT11 sensor and the SSD1306 display
4- Programming the Arduino UNO board to display the temperature and humidity measured by the DHT11 sensor on the SSD1306 display
How to use the DHT11 sensor by the Arduino UNO board ?
The DHT11 is a basic, low-cost digital temperature and humidity sensor. It's commonly used in projects that require monitoring environmental conditions. This sensor comes in a small package with four pins, and it utilizes a digital signal to communicate temperature and humidity readings to a microcontroller or a computer. The DHT11 sensor is relatively simple to use and can be found in various applications like weather stations, home automation systems, and humidity control devices.
Arduino UNO is a popular microcontroller board known for its versatility and ease of use in various electronics projects, including interfacing with DHT11 sensor. Here's a breakdown of how sensors can be used with an Arduino UNO:
Hardware Connections:
Power: Connect the DHT11 sensor's power (VCC) and ground (GND) pins to the Arduino's 5V and GND pins, respectively.
Data/Signal: the DHT11 sensor have a data pin. Connect this pin to any digital or analog pin on the Arduino (refer to the sensor's datasheet for specific pin connections).
Arduino Sketch (Code):
Utilize Arduino's programming language (based on C/C++) to interface with the sensor.
Use libraries (if available) specific to the DHT11 sensor to simplify code and access sensor readings. For instance, the Adafruit DHT library for DHT temperature and humidity sensors.
Reading Sensor Data: In the Arduino sketch, you'll write code to read data from the sensor. This might involve initializing the DHT11 sensor, reading digital values, and interpreting sensor outputs into meaningful data (temperature and humidity).
Processing Sensor Data: Display the sensor data on SSD1306 screen, serial monitor, or communicate it to other devices via Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or other communication modules connected to the Arduino.
The components required to display the temperature and humidity measured by the DHT11 sensor connected to Arduino on the SSD1306 display
To display the temperature and humidity readings from the DHT11 sensor on SSD1306 display using an Arduino, you'll need the following components:
Arduino UNO Board
The Arduino Uno board is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P microcontroller. It's one of the most popular and widely used boards in the Arduino family due to its simplicity and versatility.
It is the central control unit for your project.
DHT11 Temperature and Humidity Sensor

The DHT11 is a basic, low-cost digital temperature and humidity sensor.
SSD1306 Display

The SSD1306 is a popular display controller used in OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) screens. It's commonly employed in various electronics projects to showcase information on small screens. The SSD1306 controller is compatible with different screen sizes and is often integrated with microcontrollers like Arduino to display text, graphics, and images.
This display is used for displaying the temperature and humidity from the DHT11 sensor .
Jumper Wires:

For making temporary connections and wiring between components.
Breadboard:

A breadboard is a useful tool for creating temporary electronic circuits. It allows you to connect components without soldering.
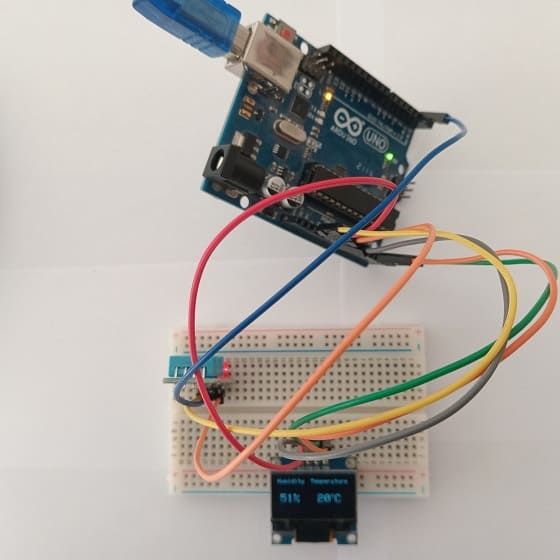
Mounting the Arduino board with the DHT11 sensor and the SSD1306 display
Mounting the Arduino board along with the DHT11 sensor and SSD1306 display can be done in various ways based on the preferences for the project's permanence, aesthetics, and convenience. Here's a suggestion on how to mount them:
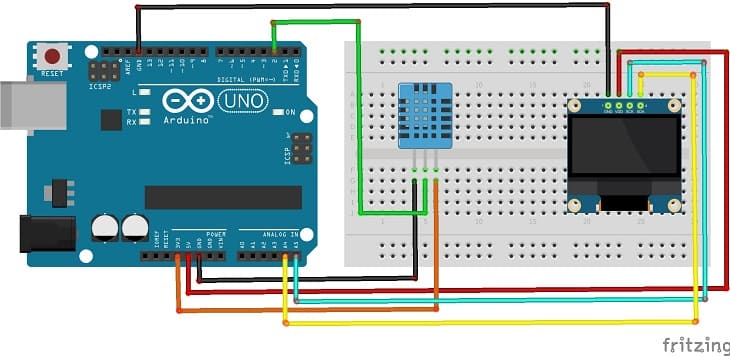
Attaching the SSD1306 Display :
- connect the VCC pin of the display to 5V pin of the Arduino
- connect the GND pin of the display to GND pin of the Arduino
- connect the SDA pin of the display to A4 pin of the Arduino
- connect the SCL pin of the display to A5 pin of the Arduino
Mounting the DHT11 Sensor:
- connect the VCC pin of the DHT11 Sensor to 3.3V pin of the Arduino
- connect the GND pin of the DHT11 to GND pin of the Arduino
- connect the DATA pin of the DHT11 to pin 2 of the Arduino
Programming the Arduino UNO board to display the temperature and humidity measured by the DHT11 sensor on the SSD1306 display
To display the temperature and humidity measured by the DHT11 sensor on SSD1306 display using an Arduino UNO, follow these steps:
1- Ensure you have the necessary libraries installed: DHT11 library and Adafruit_SSD1306 library
2- Use this code to read from the DHT11 sensor and display the temperature and humidity on the SSD1306 display.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 |
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h> #include <dht11.h> #define DHT11PIN 2 //OLED dht11 DHT11; float humi; float tempC; //OLED define #define SCREEN_WIDTH 128 // OLED display width, in pixels #define SCREEN_HEIGHT 64 // OLED display height, in pixels // Declaration for an SSD1306 display connected to I2C (SDA, SCL pins) Adafruit_SSD1306 display(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, &Wire, -1); void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); //For OLED I2C if(!display.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, 0x3C)) { // Address 0x3D for 128x64 Serial.println(F("SSD1306 allocation failed")); for(;;); } display.display(); //Display logo delay(1000); display.clearDisplay(); } void loop() { delay(1000); DHT11.read(DHT11PIN); humi = (int)DHT11.humidity; tempC = (int)DHT11.temperature; Serial.print("Humidity:"); Serial.print(humi,0); Serial.print("%"); Serial.print(" Temperature:"); Serial.print(tempC,1); Serial.print("C ~ "); display.clearDisplay(); oledDisplayHeader(); // display humidity and temperature on SSD1306 display oledDisplay(2,5,28,humi,"%"); oledDisplay(2,60,28,tempC,"C"); display.display(); } // the function displays data on SSD1306 display void oledDisplayHeader(){ display.setTextSize(1); display.setTextColor(WHITE); display.setCursor(0, 0); display.print("Humidity"); display.setCursor(60, 0); display.print("Temperature"); } void oledDisplay(int size, int x,int y, float value, String unit){ int charLen=12; int xo=x+charLen*3.2; int xunit=x+charLen*3.6; int xval = x; display.setTextSize(size); display.setTextColor(WHITE); if (unit=="%"){ display.setCursor(x, y); display.print(value,0); display.print(unit); } else { if (value>99){ xval=x; } else { xval=x+charLen; } display.setCursor(xval, y); display.print(value,0); display.drawCircle(xo, y+2, 2, WHITE); // print degree symbols ( ) display.setCursor(xunit, y); display.print(unit); } } |
Upload this code to your Arduino UNO, and the temperature and humidity readings should appear on the SSD1306 display.