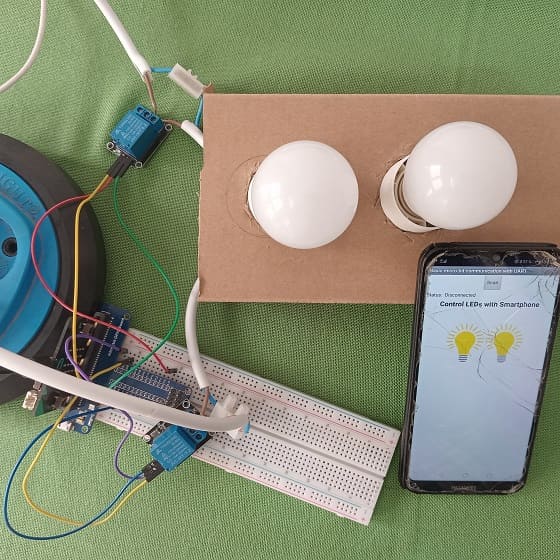
Control two lamps connected to Micro:bit via Bluetooth
Tutorial plan
1- The Micro:bit board and Bluetooth
2- Why do we use App Inventor to create a mobile application capable of communicating the smartphone with the Micro:bit board?
3- The components needed to use two lamps with Micro:bit
4- Mounting Micro:bit with two lamps
5- Programming the Microbit card to turn on two lamps via Smartphone with Makecode
6- Development of the mobile application with App Inventor to control the Micro:bit card via Smartphone
The Micro:bit board and Bluetooth
The Micro:bit is a small, programmable microcontroller board designed to teach coding and electronics to children and beginners. It was originally developed by the BBC in the United Kingdom and is now widely used in education worldwide. One of the key features of the Micro:bit is its built-in Bluetooth capability, which allows it to communicate with other devices and be used in various applications.
Here are some important aspects of the Micro:bit's Bluetooth functionality:
Bluetooth Version: The Micro:bit uses Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology, which is a power-efficient version of Bluetooth suitable for battery-operated devices. BLE is commonly used for connecting devices like smartphones, tablets, and other microcontrollers.
Bluetooth Radio: The Micro:bit has a built-in Bluetooth radio module that allows it to both send and receive data wirelessly. This radio module is used for communication between the Micro:bit and other devices.
Bluetooth Pairing: To connect the Micro:bit to another device, such as a smartphone or another Micro:bit, you typically need to pair them. Pairing involves establishing a secure connection between the devices to ensure data privacy and security.
Programming Bluetooth: The Micro:bit can be programmed to use Bluetooth for various purposes. For example, you can create programs that allow the Micro:bit to send sensor data (e.g., temperature, accelerometer data) to a smartphone app or receive commands from a smartphone to control LEDs or other outputs on the Micro:bit.
Block-based and Text-based Programming: Programming the Micro:bit with Bluetooth capabilities can be done using block-based programming languages like MakeCode and text-based languages like MicroPython. MakeCode is a popular choice for beginners due to its visual, drag-and-drop interface, while MicroPython offers more advanced programming capabilities.
Applications: With its Bluetooth capabilities, the Micro:bit can be used in a wide range of applications. For example, it can be used to create remote-controlled cars, interactive games, fitness trackers, weather stations, and more. Its small size and ease of programming make it versatile for various educational and hobbyist projects.
Bluetooth Accessories: There are also accessories and expansion boards available that can extend the Micro:bit's Bluetooth functionality. These accessories can add features such as motor control, additional sensors, and more, enabling even more diverse projects.
In summary, the Micro:bit's built-in Bluetooth functionality makes it a powerful tool for teaching programming and electronics while also allowing for creative and practical projects that involve wireless communication. It's a great platform for beginners and educators to explore the world of coding and electronics.
Why do we use App Inventor to create a mobile application capable of communicating the smartphone with the Micro:bit board ?
MIT App Inventor is a visual programming environment that allows people with little to no programming experience to create mobile applications for Android devices. It's particularly well-suited for educational purposes and rapid prototyping. Here's why App Inventor is often used to create applications for communicating with the Micro:bit board:
Visual Interface: App Inventor provides a visual interface for designing the user interface and behavior of mobile applications. This means you can create applications by dragging and dropping components (like buttons, labels, etc.) and visually connecting them to define their behavior. This makes it accessible to beginners who might find traditional text-based programming intimidating.
Simplicity and Accessibility: App Inventor uses a blocks-based programming model, which means you create applications by snapping together blocks that represent actions, events, and functions. This is more intuitive for beginners and can be a less daunting way to start programming.
Integration with Hardware Components: App Inventor has built-in support for Bluetooth communication. This makes it relatively straightforward to create apps that can communicate with external devices like the Micro:bit. It provides a Bluetooth component that simplifies the process of establishing connections and sending/receiving data.
Immediate Testing: You can connect your Android device to App Inventor via USB or over Wi-Fi, allowing you to instantly test your applications on your phone. This immediate feedback loop is crucial for learning and debugging.
Educational Focus: MIT App Inventor was designed with educational purposes in mind. It's used in schools and educational programs around the world to teach programming concepts and mobile app development. Its simplicity and visual approach make it an excellent choice for introducing students to the world of programming and electronics.
Community and Resources: There's a vibrant community around MIT App Inventor, which means there are plenty of tutorials, forums, and resources available to help beginners get started and troubleshoot any issues they encounter.
Cross-Platform Support: While App Inventor itself is a web-based tool, the apps you create can be installed on Android devices. This makes it accessible to a wide range of users who have Android smartphones or tablets.
In the context of Micro:bit communication, using App Inventor allows educators and beginners to create applications that can control or interact with the Micro:bit without the need for extensive programming knowledge. It provides a user-friendly platform for learning and experimenting with both mobile app development and hardware interaction.
The components needed to control two lamps by Micro:bit board
To control a lamp using a Micro:bit board, you'll need a few components to set up a safe and functional circuit. Here's a list of the necessary components:
Micro:bit Board:
The Micro:bit board, often referred to simply as the Micro:bit, is a small, programmable microcontroller designed for educational purposes and hands-on learning.
The GPIO expansion card for the Micro:bit card

The GPIO expansion board for the Micro:bit board expands the capabilities of the Micro:bit board by adding more input/output (GPIO) pins and additional functionality.
Two Relays Module:
The relay plays a crucial role in controlling high-power or high-voltage devices like lamps using a microcontroller such as the Micro:bit. The Micro:bit, being a low-power device, cannot directly control these high-power devices due to differences in voltage and current requirements.
The relay acts as a switch that is controlled by the Micro:bit. When the Micro:bit sends a signal (typically a digital signal) to the relay module, the relay switches its internal contacts, allowing or interrupting the flow of electricity to the lamp.
Two lamps (220V):

The lamp you want to control, which is rated for 220V. Ensure it's in working condition and safe to use.
Power Supply for the Lamp:

You'll need a power source for the lamp, typically a 220V AC power supply.
Wiring:

Various wires and cables for connecting the components in your circuit.
Breadboard or Prototyping Board (optional):

A breadboard can be useful for creating temporary connections and organizing your circuit.
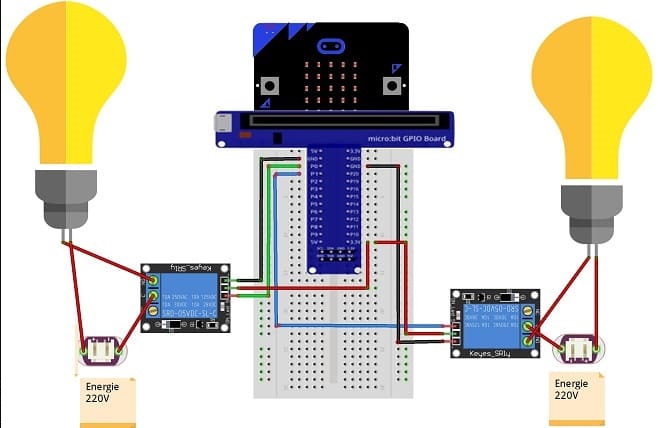
Mounting the Micro:bit board with two lamps
To control two lamps using a Micro:bit board, you will need to use a relay module to safely interface the low-voltage Micro:bit with the high-voltage lamp. Here are the step-by-step instructions to set up the Micro:bit with two lamps:
1- Safety First: Ensure the lamp is disconnected from any power source before proceeding.
2- Connect the first Relay to the Micro:bit:
- Connect the relay's control pin (S) to pin P0 of Micro:bit board
- Connect the pin (+) of relay to pin 3.3V of Micro:bit board.
- Connect the relay's ground pin (GND) to the Micro:bit's GND.
3- Connect the first Lamp and the power supply to the Relay:
- Connect one of the lamp's wires to the normally open (NO) terminal of the relay.
- Connect the phase wire of the power supply to the relay's common (COM) terminal.
- Connect the neutral wire of the power supply directly to the neutral wire of the lamp.
4- Connect the second Relay to the Micro:bit:
- Connect the relay's control pin (S) to pin P1 of Micro:bit board
- Connect the pin (+) of relay to pin 3.3V of Micro:bit board.
- Connect the relay's ground pin (GND) to the Micro:bit's GND.
5- Connect the second Lamp and the power supply to the Relay:
- Connect one of the lamp's wires to the normally open (NO) terminal of the relay.
- Connect the phase wire of the power supply to the relay's common (COM) terminal.
- Connect the neutral wire of the power supply directly to the neutral wire of the lamp.
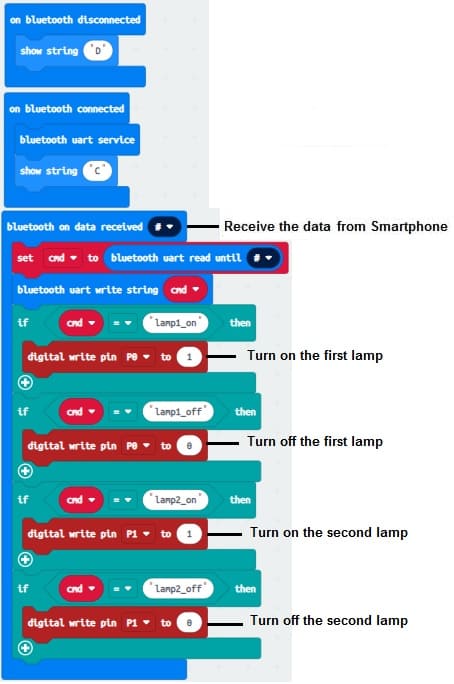
Programming the Microbit card to turn on two lamps via Smartphone with Makecode
To control two lamps connected to the Micro:bit board by two relays , you can use MakeCode to program the Micro:bit3 Here are the steps to do this:
1- Go to the MakeCode website for the Micro:bit (https://makecode.microbit.org/).
2- Create a new project.
3- In the "Blocks" view, under "Bluetooth," add the "on Bluetooth connected" block to handle Bluetooth connections.
4- Set the pin "0" to "1" to turn on the first lamp if the Micro:bit card receives the word 'lamp1_on'
5- Duplicate the "digital write pin" block and set the pin "0" to "0" to turn off the first lamp when the Micro:bit card receives the word 'lamp1_off'.
6- Set the pin "0" to "1" to turn on the second lamp if the Micro:bit card receives the word 'lamp2_on'
7- Duplicate the "digital write pin" block and set the pin "0" to "0" to turn off the second lamp when the Micro:bit card receives the word 'lamp2_off'.
8- Your code might look something like this:
Development of the mobile application with App Inventor to control the Micro:bit card via Smartphone
Creating the MIT App Inventor Mobile App:
1- Go to the MIT App Inventor website (http://ai2.appinventor.mit.edu/).
2- Create a new project.
3- Design a simple interface with two buttons to turn the two lamps on and off.
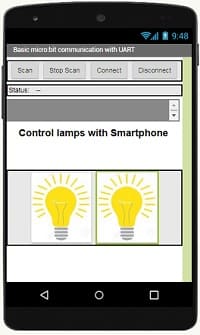
4- Design the user interface of your app. You might have two buttons to turn on and turn off the two lamps
5- Add the components to your app. ![]()
- The "BluetoothLE1" extension indeed refers to a specific extension for MIT App Inventor which allows you to manage Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) communication in your mobile applications. This extension facilitates the interaction between your App Inventor application and BLE devices, such as sensors, trackers, wearables, etc.
- The "BluetoothClient1" extension in MIT App Inventor allows you to create mobile applications that can connect to Bluetooth devices, such as serial Bluetooth modules (eg HC-06) connected to microcontrollers, Bluetooth audio devices, etc. . This extension facilitates communication with these devices using serial Bluetooth connections.
- The "Microbit_UART1" extension allows you to use UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) communication with the Micro:bit card in the MakeCode programming environment.
- The "Notifier1" extension in MIT App Inventor is a component for displaying notifications or messages to the user of an application. It can be used to send pop-up messages, alerts or important information to the user while the application is running. It is a useful component to improve user experience by providing contextual information.
MIT App Inventor Blocks
1- Starting with Android 12, Bluetooth permissions have been enhanced to improve security and user data protection. This is why we must declare the authorizations that your application needs in the AndroidManifest.xml file. For Bluetooth, you'll need to include ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION, BLUETOOTH_SCAN, and possibly BLUETOOTH_CONNECT permissions, depending on the features you're using.
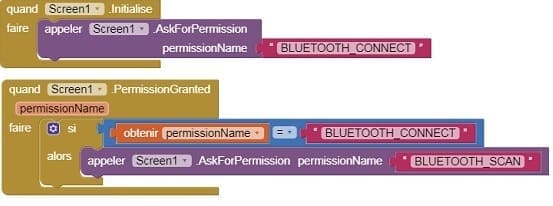
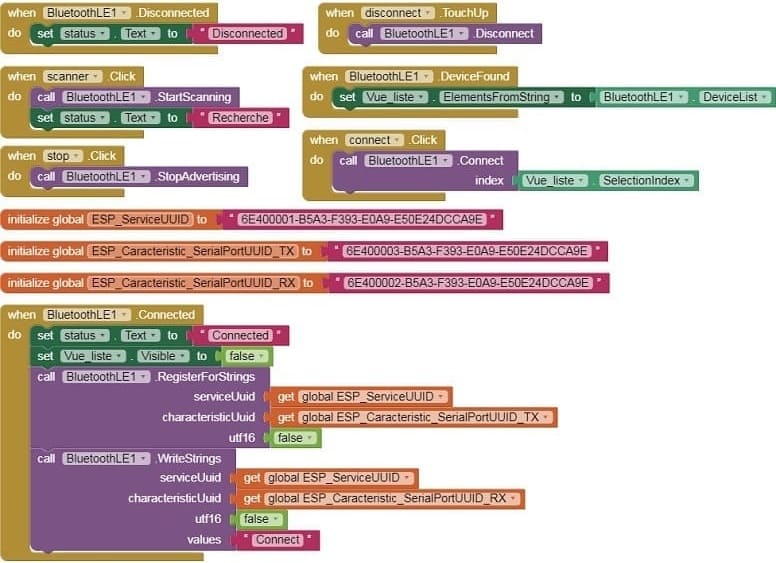
2- Use these programming blocks to connect the smartphone to the Micro:bit board via Bluetooth:
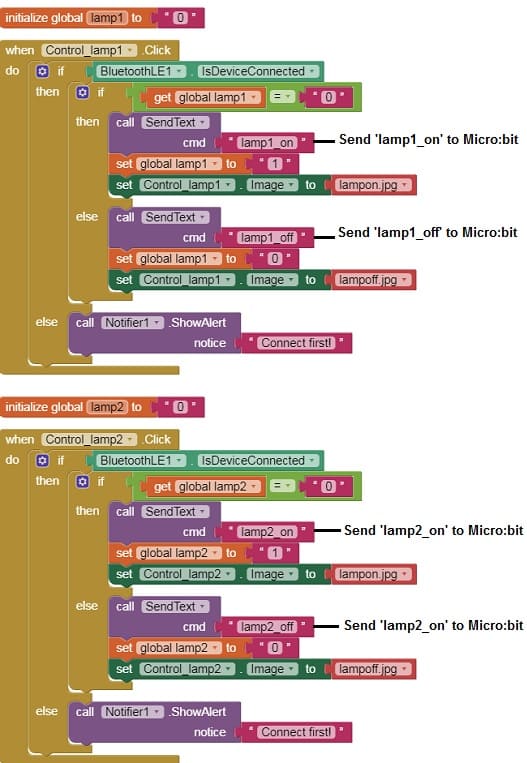
3- Use programming blocks to send Bluetooth commands to the Micro:bit when the button is clicked.
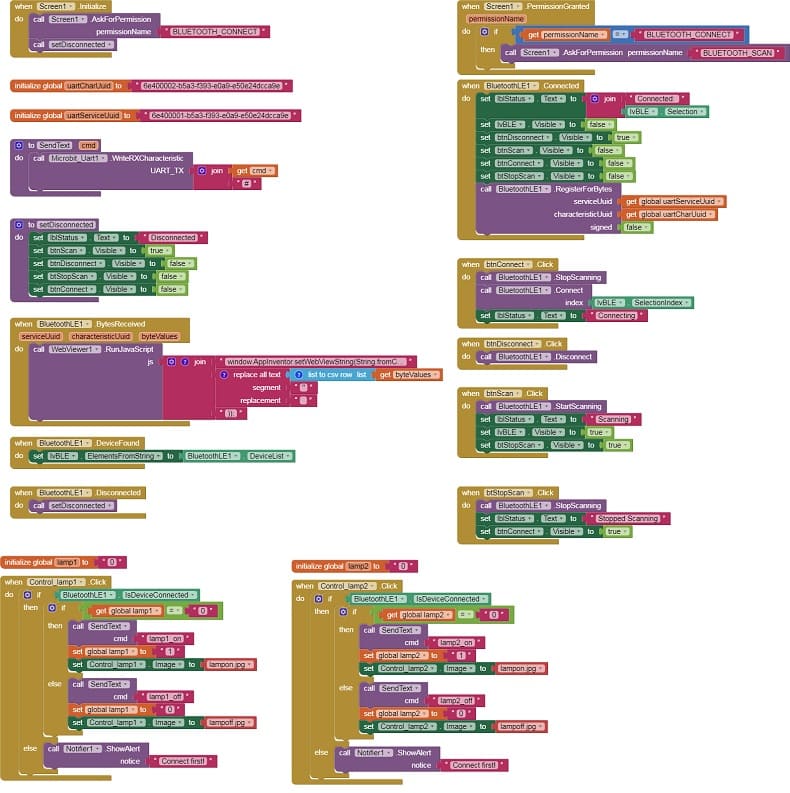
Here is the final program of the mobile application :
Download projectDownload apk file
5. Test:
- Load the Makecode code onto your Micro:bit.
- Install the MIT App Inventor app on your smartphone and install the app you created.
- Pair and connect your smartphone with the Micro:bit through Bluetooth.
- Open the app and use the buttons to control the two lamps connected to the Micro:bit.
With these steps completed, you should be able to control the lamps on your Micro:bit from your smartphone via Bluetooth.
Pressing the first button in the app should turn on the first lamp, and pressing again the button should turn off the lamp.
Pressing the second button in the app should turn on the second lamp, and pressing again the button should turn off the lamp.
























