Control a lamp connected to the ESP32 board via Bluetooth
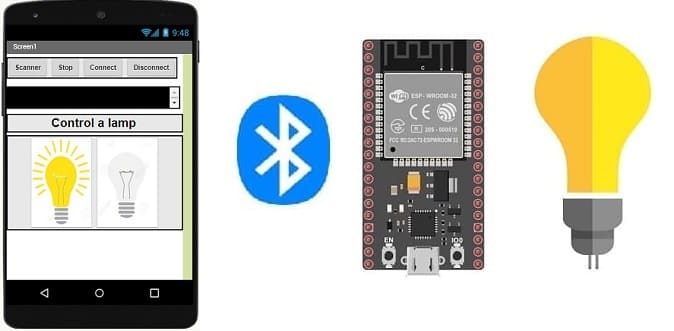
Tutorial plan
1- Why do we use App Inventor to create a mobile application capable of communicating the smartphone with the ESP32 board?
2- The components needed to control a lamp with the ESP32 board
3- Mounting the ESP32 board with a lamp and a relay
4- Lighting a lamp connected to the ESP32 board by a smartphone via Bluetooth using the Micropython and MIT Inventor app
Why do we use App Inventor to create a mobile application capable of communicating the smartphone with the ESP32 board?
App Inventor is a visual programming environment that simplifies the process of creating Android applications. It's particularly useful for beginners or those without extensive programming experience because of its block-based interface, which allows users to drag and drop visual blocks to create functionalities instead of writing code from scratch.
When it comes to communicating with an ESP32 board (or any hardware) from a smartphone, App Inventor provides a user-friendly interface to create apps that can interact with hardware via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. Here's why it's commonly used for this purpose:
Ease of Use: App Inventor's block-based system makes it easy to create mobile apps without requiring extensive coding knowledge. It simplifies the process of creating UI elements, defining behaviors, and handling interactions.
Visual Interface: Its visual interface allows users to create apps by assembling blocks that represent different functionalities. This makes it more intuitive and accessible compared to traditional text-based coding.
Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Support: App Inventor provides built-in components and blocks that allow easy integration with Bluetooth or Wi-Fi modules, which are commonly used for communication with devices like the ESP32.
Rapid Prototyping: For quick prototyping or proof-of-concept projects, App Inventor enables fast development cycles. Users can quickly iterate and test functionalities before moving on to more complex development stages.
Community Support: It has a supportive community with resources, tutorials, and forums where users can find help, share ideas, and troubleshoot issues related to integrating hardware with mobile apps.
The components needed to control a lamp by ESP32 card
To control a lamp using the ESP32 board, you will need the following components:
ESP32 Board:
The ESP32 is a microcontroller board that features built-in WiFi and Bluetooth capabilities. It can be programmed and used to control the lamp.
Relay Module:
You'll need a relay module that is compatible with the ESP32 card and can switch the high-voltage lamp. Ensure it's rated for the voltage and current required for your lamp.
Lamp (220V):

The lamp you want to control, which is rated for 220V. Ensure it's in working condition and safe to use.
Power Supply for the Lamp:

You'll need a power source for the lamp, typically a 220V AC power supply.
Wiring:

Various wires and cables for connecting the components in your circuit.
Breadboard:

A breadboard is a prototyping board that allows you to build circuits without soldering. It provides a convenient way to connect the components together.
Jumper Wires:

You'll need jumper wires to make connections between the ESP32 card, lamp, relay, and breadboard. Ensure you have male-to-male jumper wires or a mix of male-to-male and male-to-female wires, depending on your specific needs.
Mounting the ESP32 card with a lamp and a relay
To control a lamp using a ESP32 board, you will need to use a relay module to safely interface the low-voltage ESP32 card with the high-voltage lamp. Here are the step-by-step instructions to set up the ESP32 with a lamp:
1- Safety First: Ensure the lamp is disconnected from any power source before proceeding.
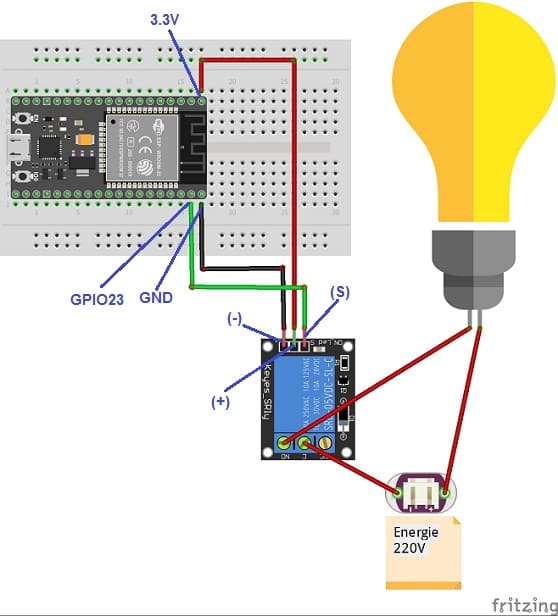
2- Connect the Relay to the ESP32:
- Connect the relay's control pin (S) to pin 23 of ESP32 board.
- Connect the pin (+) of relay to pin 3.3V of ESP32 board.
- Connect the relay's ground pin (GND) to the ESP32's GND.
3- Connect the Lamp and the power supply to the Relay:
- Connect one of the power supply's wires to the relay's common (COM) terminal.
- Connect the phase wire of the the lamp to the normally open (NO) terminal of the relay.
- Connect the neutral wire of the power supply directly to the neutral wire of the lamp.
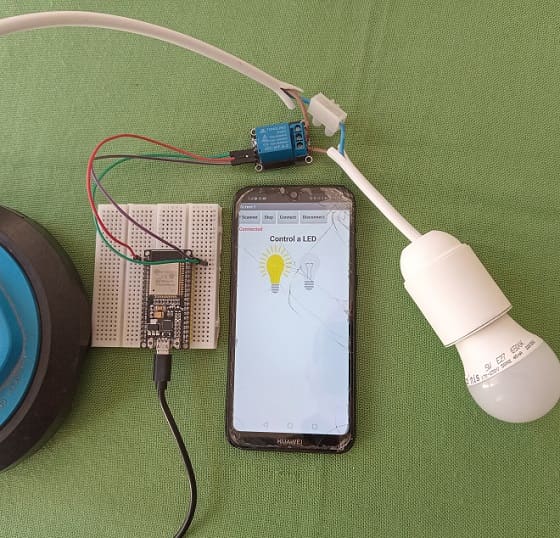
Lighting a lamp connected to the ESP32 board by a smartphone via Bluetooth using the Micropython and MIT Inventor app
To light a lamp connected to an ESP32 board using a smartphone via Bluetooth, you can follow these steps using MicroPython for the ESP32 and the MIT App Inventor:
1. ESP32 MicroPython Code:
Write a simple MicroPython script to control the lamp using Bluetooth.
You'll need to use ble_uart_peripheral.py and ble_advertising.py.
you must use the following firmware: esp32-20210902-v1.17.bin .
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
########## DIGITAL MANUFACTURING ########## # PIKACHU Project # Authors: Miguel Angel Guzman # Kadriye Nur Bakirci ########################################### ########## IMPORT REQUIRED LIBRARIES ########## import bluetooth from ble_uart_peripheral import BLEUART from machine import Pin relay_pin=Pin(23, Pin.OUT) # GPIO pin connected to the relay # Create BLE object ble = bluetooth.BLE() # Open UART session for BLE uart = BLEUART(ble) # Define ISR for an UART input on BLE connection def on_rx(): # Read UART string, AppInventor sends raw bytes uart_in = uart.read() # read the message received from the Smartphone via Bluetooth print("UART IN: ", uart_in.decode()) # display the message received from the Smartphone on the Thonny console if (uart_in.decode().find('1')==0): relay_pi.value(1) # Turn on the lamp if (uart_in.decode().find('0')==0): relay_pi.value(0) # Turn off the lamp # Map ISR to UART read interrupt uart.irq(handler=on_rx) uart.close() |
2. MIT App Inventor Setup:
1- Create a new project in MIT App Inventor.
2- Add the BluetoothClient component to your project.
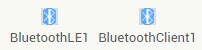
- The "BluetoothLE1" extension indeed refers to a specific extension for MIT App Inventor which allows you to manage Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) communication in your mobile applications. This extension facilitates the interaction between your App Inventor application and BLE devices, such as sensors, trackers, wearables, etc.
- The "BluetoothClient1" extension in MIT App Inventor allows you to create mobile applications that can connect to Bluetooth devices, such as serial Bluetooth modules (eg HC-06) connected to microcontrollers, Bluetooth audio devices, etc. . This extension facilitates communication with these devices using serial Bluetooth connections.
3- Starting with Android 12, Bluetooth permissions have been enhanced to improve security and user data protection. This is why we must declare the authorizations that your application needs in the AndroidManifest.xml file. For Bluetooth, you'll need to include ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION, BLUETOOTH_SCAN, and possibly BLUETOOTH_CONNECT permissions, depending on the features you're using.
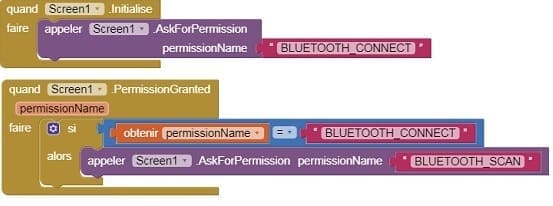
4- Use these programming blocks to connect the smartphone to the ESP32 board via Bluetooth:
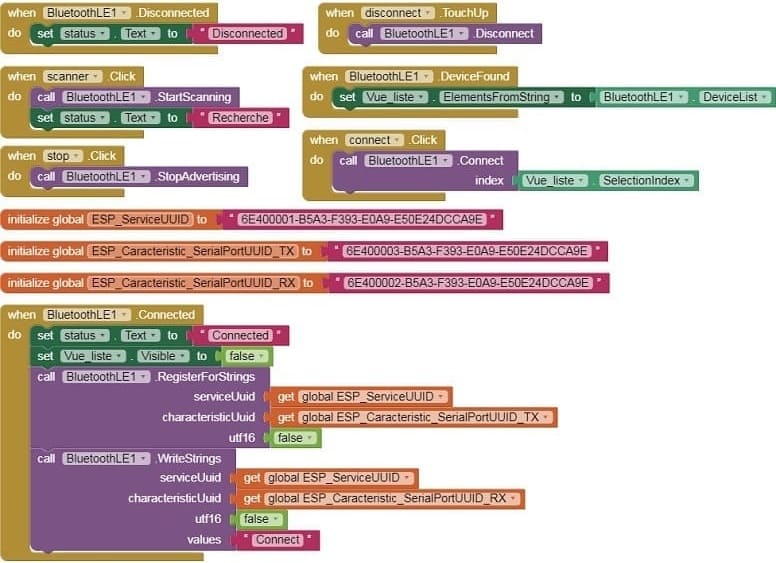
4. MIT App Inventor Blocks:
- Design a simple interface with two buttons to turn the lamp on and off.
- Use programming blocks to send Bluetooth commands to the ESP32 when the button is clicked.
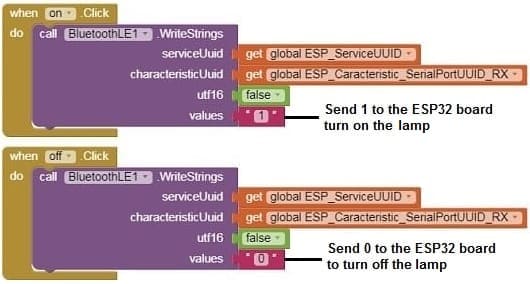
Here's a complete example of what this might look like in App Inventor:
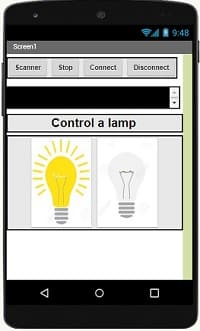
Designer part of the mobile application
Program part of the mobile application

Download aia projectDownload apk file
5. Test:
- Load the MicroPython code onto your ESP32.
- Install the MIT App Inventor app on your smartphone and install the app you created.
- Pair and connect your smartphone with the ESP32 through Bluetooth.
- Open the app and use the button to control the lamp connected to the ESP32 by a relay.