RFID based access control system with ESP8266 NodeMCU
Tutorial plan
1- What is an access control system ?
2- Presentation of RFID based access control system by ESP8266
3- Required Components
4- Circuit Connections of system
5- Micropython program of system
What is an access control system ?
An access control system is a security mechanism that regulates who or what can enter or exit a specific area, system, or resource. It is commonly used to protect buildings, restricted areas, digital systems, and confidential data.
Types of Access Control Systems
1. Physical Access Control – Controls access to physical locations, such as buildings, offices, or rooms, using devices like:
RFID cards and readers
Keypads and PIN codes
Biometrics (fingerprint, facial recognition)
Smart locks and electronic doors
2. Logical Access Control – Controls access to digital resources, such as:
Computer systems and networks
Files and databases
Cloud services and applications
How It Works
1. Authentication – The system verifies the identity of the user via a credential (e.g., RFID card, password, fingerprint).
2. Authorization – If the credential is valid, the system checks whether the user has permission to access the resource.
3. Access Grant/Denial – If authorized, access is granted; otherwise, access is denied.
4. Logging & Monitoring – The system records access attempts for security auditing.
Examples of Access Control Systems
Office entry systems using RFID badges
Fingerprint-based access to mobile devices
Secure login systems with multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Smart home locks controlled by mobile apps
Presentation of RFID based access control system by ESP8266
An RFID access control system is a security system that uses Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to grant or restrict access to a secured area, device, or system. It works by using RFID tags (such as keycards or fobs) and RFID readers to authenticate users.
Our system uses an RFID card or key fob to authenticate users and either grant or deny access based on a stored list of authorized IDs. The LCD I2C display shows access messages.
How It Works
1- User presents an RFID card/tag to the RC522 RFID reader.
2- RFID reader reads the unique ID (UID) stored in the RFID tag.
3- ESP8266 processes the UID and checks if it matches a list of authorized IDs stored in its memory.
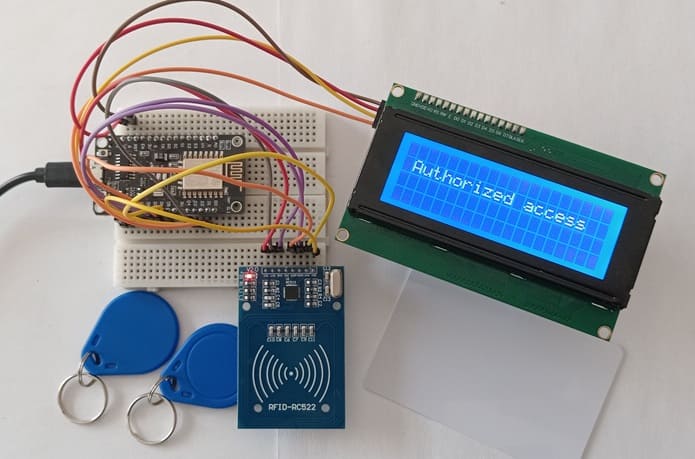
4- If UID is authorized: The LCD displays “Access Granted”
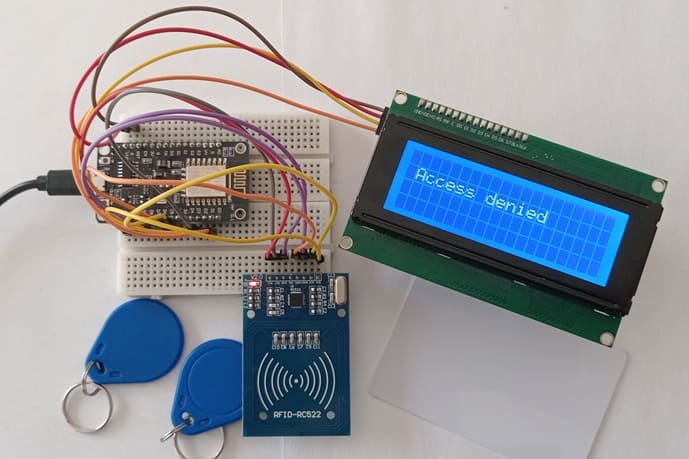
5- If UID is NOT authorized: The LCD displays “Access Denied”
Required Components
ESP8266 NodeMCU (Microcontroller)

- Acts as the brain of the system.
- Reads data from the RFID RC-522 module.
- Checks the UID (Unique Identifier) of the RFID tag against stored values.
- Controls LCD I2C display to show messages.
RFID Module RC-522

- Reads the RFID card/tag using radio frequency signals.
- Communicates with ESP8266 via SPI protocol.
- Retrieves UID from the card and sends it to the microcontroller.
RFID Tags or Cards


- Acts as the user identification key.
- Each card has a unique UID (e.g., 0xABC12345).
- When scanned, the UID is sent to ESP8266 for authentication.
LCD I2C Display
- Displays system messages such as "Scan Your Card", "Access Granted", or "Access Denied".
Breadboard:

- Provides a temporary connection for components without soldering.
Jumper Wires:

- Used to connect ESP8266, RFID module, LCD, relay, buzzer, and LEDs.
Circuit Connections of system
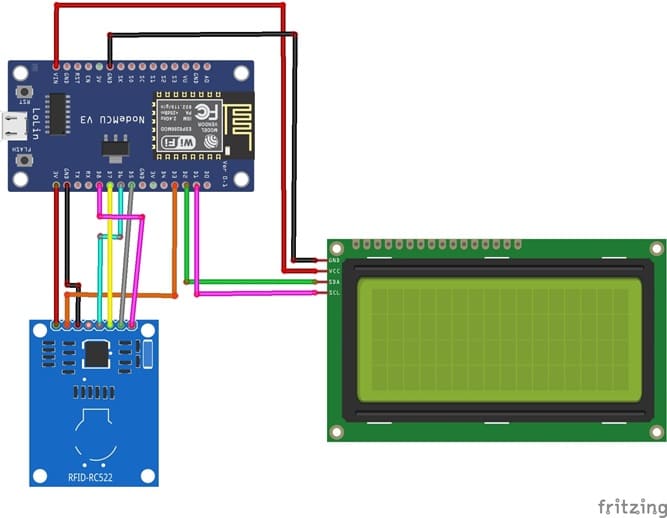
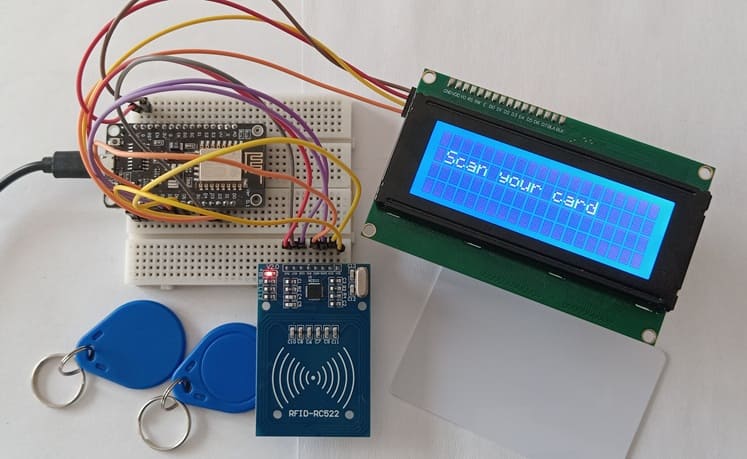
RFID-RC522 to ESP8266 NodeMCU connections
RFID-RC522 Pin | ESP8266 NodeMCU Pin |
SDA | GPIO 15 (D8) |
SCK | GPIO 14 (D5) |
MOSI | GPIO 13 (D7) |
MISO | GPIO 12 (D6) |
GND | GND |
RST | GPIO 0 (D3) |
3V3 | 3V3 |
I2C LCD to ESP8266 NodeMCU connections
LCD I2C Screen Pin | ESP8266 NodeMCU Pin |
VCC | VIN |
GND | GND |
SDA | GPIO 4 (D2) |
SCL | GPIO 5 (D1) |
Micropython program of system
Before running the code, install the necessary libraries:
- MFRC522 (for RFID module)
- i2c_lcd and lcd_api for I2C LCD screen
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 |
import machine from machine import Pin, SoftI2C,ADC,SPI from lcd_api import LcdApi from i2c_lcd import I2cLcd from mfrc522 import MFRC522 from time import sleep_ms sck = Pin(14, Pin.OUT) mosi = Pin(13, Pin.OUT) miso = Pin(12, Pin.OUT) sda = Pin(15, Pin.OUT) spi = SPI(baudrate=100000, polarity=0, phase=0, sck=sck, mosi=mosi, miso=miso) I2C_ADDR = 0x27 totalRows = 4 totalColumns = 20 i2c = SoftI2C(sda=Pin(4), scl=Pin(5), freq=400000) #D2(SDA) D1(SCL) #initializing the I2C method for ESP32 lcd = I2cLcd(i2c, I2C_ADDR, totalRows, totalColumns) def do_read(): while True: rdr = MFRC522(spi, sda) uid = "" (stat, tag_type) = rdr.request(rdr.REQIDL) if stat == rdr.OK: (stat, raw_uid) = rdr.anticoll() if stat == rdr.OK: uid = ("0x%02x%02x%02x%02x" % (raw_uid[0], raw_uid[1], raw_uid[2], raw_uid[3])) print(uid) lcd.clear() lcd.move_to(1,1) # The ESP8266 compares the UID with the UID stored in the code if uid=="0xdb1bb201" : lcd.putstr("Authorized access") else: lcd.putstr("Access denied") sleep_ms(5000) lcd.clear() lcd.move_to(1,1) lcd.putstr('Scan your card') else: dui="" lcd.clear() lcd.move_to(1,1) lcd.putstr('Scan your card') do_read() |