ESP32 boat controlled by Wifi
Tutorial plan
1- Objective of building ESP32 robot boat
2- Required Components
3- Boat Wiring Diagram
4- Micropython program for ESP32
Objective of building ESP32 robot boat
The objective of building an ESP32 robot boat controlled by Wi-Fi using a water pump, relay module, and servo motor is to develop a versatile, remotely controlled aquatic vehicle capable of performing a variety of tasks.
The ESP32 connects to a Wi-Fi network and hosts a web-based interface or uses a mobile app (Blynk, MQTT, etc.) to receive user commands. These commands control the water pump (for propulsion) and the servo motor (for direction control).
a. Propulsion System (Water Pump + Relay)
1- The ESP32 sends a signal to the relay module.
2- The relay activates the water pump, allowing water to be expelled, pushing the boat forward.
3- The pump can be turned ON/OFF via commands.
b. Direction Control (Servo Motor)
1- The ESP32 sends PWM signals to the servo motor.
2- The servo rotates the rudder, changing the boat's direction.
3- Left (0°–45°), Right (135°–180°), Center (90°).
c. Wi-Fi Control Mechanism
The ESP32 creates a Wi-Fi Access Point (AP Mode) or connects to an existing Wi-Fi network (Station Mode).
A web server runs on the ESP32, providing a control interface.
The user accesses the web dashboard via a smartphone, tablet, or PC.
Button presses send commands via HTTP requests/WebSocket, controlling the relay and servo.
Required Components
ESP32 Microcontroller:

Acts as the central brain of the boat.
Manages all peripherals, including the water pump, relay module, and servo motor.
Hosts or connects to a Wi-Fi network, allowing control via a smartphone or computer.
Water Pump:

Provides propulsion by expelling water through a nozzle.
Responsible for moving the boat forward or backward by changing the pump's orientation or water flow direction.
Relay Module:
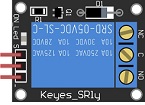
Controls the water pump by switching it on or off as per commands from the ESP32.
Acts as an intermediary between the ESP32 and the high-current motor of the water pump.
Servo Motor:
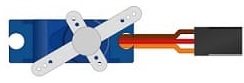
Controls the steering by adjusting the rudder or the direction of the water pump nozzle.
Operates based on angle values sent by the ESP32, enabling precise directional control.
3V/5V power module

It supplies a stable 5V with sufficient current for the boat.
Power Supply:
Provides adequate power for the ESP32, water pump, servo motor, and relay module.
Typically uses a battery pack with appropriate voltage (e.g., 7.4V or 12V, depending on the components).
Jumper Wires :

Jumper wires will be used to make connections between the components.
Breadboard (Optional):

A breadboard is a versatile and reusable platform used for prototyping and testing electronic circuits without the need for soldering.
Boat Wiring Diagram
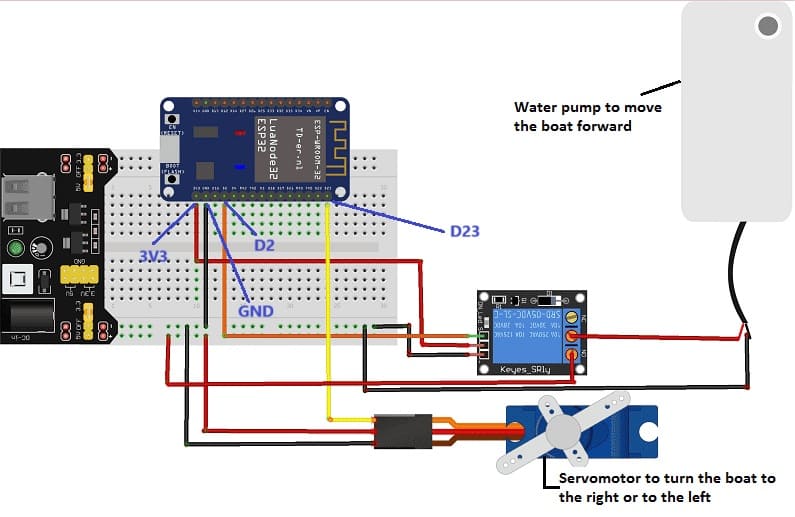
we connect :
1- for the servomotor:
- the yellow wire to pin 2 of the ESP32 board
- the red wire to the 5V pin of the power supply module
- the black wire to the GND pin of the ESP32 board.
2- for relay:
- we connect pin (S) to pin 23 of the ESP32 board
- we connect pin (+) to the 3.3V pin of the ESP32 board
- we connect the pin (-) to the GND pin of the ESP32 board
- Connect the COM pin to the (+) terminal of the water pump
- Connect the NO pin to the 5V terminal of the power supply module
3- for the water pump:
the (-) terminal to the GND pin of the ESP32 board.
Micropython program for ESP32
Here are 2 micropython programs that allow you to connect the ESP32 card to the smartphone via the wifi network and to receive a message containing the command order of the boat.
You must install the servo library for the servo motor.
1- boot.py
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
# Complete project details at https://RandomNerdTutorials.com import machine try: import usocket as socket except: import socket from machine import Pin import network from servo import Servo import esp esp.osdebug(None) import gc gc.collect() ssid = '*************' # pour la connexion de la carte ESP32 au réseau wifi password = '*************' station = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF) station.active(True) station.connect(ssid, password) while station.isconnected() == False: pass print('Connection successful') print(station.ifconfig()) pompe = Pin(2, Pin.OUT) servo_pin = machine.Pin(23) my_servo = Servo(servo_pin) |
2- main.py
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 |
# Complete project details at https://RandomNerdTutorials.com def web_page(): if pompe.value() == 1: gpio_state="ON" else: gpio_state="OFF" html = """<html><head> <title>ESP Web Server</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <link rel="icon" href="data:,"> <style>html{font-family: Helvetica; display:inline-block; margin: 0px auto; text-align: center;} h1{color: #0F3376; padding: 2vh;}p{font-size: 1.5rem;}.button{display: inline-block; background-color: #e7bd3b; border: none; border-radius: 4px; color: white; padding: 16px 30px; text-decoration: none; font-size: 20px; margin: 2px; cursor: pointer;} .button2{background-color: red;}</style></head><body> <h1>ESP Web Server</h1> <p>GPIO state: <strong>""" + gpio_state + """</strong></p><p><a href="/?pompe=on"><button class="button">Avant</button></a></p> <table><tr><td><p><a href="/?pompe=gauche"><button class="button">Gauche</button></a></p></td><td><p><a href="/?pompe=off"><button class="button button2">Stop</button></a></p></td> <td><p><a href="/?pompe=droite"><button class="button">Droite</button></a></p></td> </tr></table></body></html>""" return html s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) s.bind(('', 80)) s.listen(5) while True: conn, addr = s.accept() print('Got a connection from %s' % str(addr)) request = conn.recv(1024) request = str(request) print('Content = %s' % request) pompe_on = request.find('/?pompe=on') pompe_off = request.find('/?pompe=off') pompe_droite = request.find('/?pompe=droite') pompe_gauche = request.find('/?pompe=gauche') if pompe_on == 6: print('LED ON') pompe.value(1) my_servo.write_angle(90) if pompe_off == 6: print('LED OFF') pompe.value(0) if pompe_droite == 6: print('LED ON') pompe.value(1) my_servo.write_angle(45) if pompe_gauche == 6: print('LED ON') pompe.value(1) my_servo.write_angle(135) response = web_page() conn.send('HTTP/1.1 200 OK\n') conn.send('Content-Type: text/html\n') conn.send('Connection: close\n\n') conn.sendall(response) conn.close() |
How It Works
1. Wi-Fi AP Mode: ESP32 creates a Wi-Fi network ESP32-Boat, password: 12345678.
2. Web Interface: Access 192.168.4.1 in a web browser.
3. Control Buttons:
Stop: Turns the relay OFF (stopping the pump).
Turn Left: Moves the servo to 45° (left rudder).
Center: Moves the servo to 90° (straight rudder).
Turn Right: Moves the servo to 135° (right rudder).
4. ESP32 Handles HTTP Requests and controls relay & servo motor accordingly.
15 comments
buy wallet.dat 07-03-2626
I've read several just right stuff here. Certainly price bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how a lot effort you put to make any such excellent informative website.
sx lawyers 03-03-2626
Greetings from Idaho! I'm bored to tears at work so I decided to browse your blog on my iphone during lunch break. I love the info you provide here and can't wait to take a look when I get home. I'm shocked at how fast your blog loaded on my phone .. I'm not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, superb site!
buy wallet.dat 02-03-2626
Definitely believe that that you stated. Your favorite justification appeared to be on the net the simplest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I definitely get annoyed while other folks think about concerns that they just don't realize about. You controlled to hit the nail upon the highest as neatly as defined out the entire thing with no need side effect , people could take a signal. Will probably be again to get more. Thank you
Gudang Database Store 12-02-2626
Excellent blog here! Additionally your site rather a lot up very fast! What host are you the use of? Can I get your associate hyperlink on your host? I want my website loaded up as fast as yours lol
https://www.sxlawyers.com 06-02-2626
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your articles as long as I provide credit and sources back to your blog? My blog site is in the exact same area of interest as yours and my users would truly benefit from a lot of the information you present here. Please let me know if this alright with you. Thanks!
sx lawyers 03-02-2626
Hmm is anyone else experiencing problems with the pictures on this blog loading? I'm trying to find out if its a problem on my end or if it's the blog. Any responses would be greatly appreciated.
Data pemain Judi di Indonesia 28-01-2626
Hello, i think that i saw you visited my site so i came to “return the favor”.I am trying to find things to improve my site!I suppose its ok to use some of your ideas!!
bitcoin wallet dat 20-01-2626
I'm no longer positive the place you're getting your info, however good topic. I must spend some time learning much more or figuring out more. Thanks for fantastic info I was searching for this info for my mission.
sx lawyers 06-01-2626
I do trust all the concepts you have introduced in your post. They are very convincing and will definitely work. Nonetheless, the posts are very short for beginners. Could you please extend them a little from subsequent time? Thank you for the post.
lawyers near me 28-12-2525
I like the helpful information you provide in your articles. I will bookmark your weblog and check again here regularly. I am quite certain I will learn lots of new stuff right here! Good luck for the next!
situs togel resmi 16-12-2525
Wow, this article is nice, my younger sister is analyzing such things, thus I am going to let know her.
ginsengtoto 16-12-2525
I'm amazed, I must say. Rarely do I come across a blog that's both educative and entertaining, and let me tell you, you've hit the nail on the head. The issue is something not enough men and women are speaking intelligently about. I am very happy that I found this during my hunt for something relating to this.
situs togel resmi 15-12-2525
It's wonderful that you are getting ideas from this post as well as from our dialogue made here.
GINSENGOTO 12-12-2525
It's a pity you don't have a donate button! I'd certainly donate to this fantastic blog! I suppose for now i'll settle for book-marking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to new updates and will talk about this blog with my Facebook group. Chat soon!
ginsengtoto link alternatif 04-12-2525
What's up, this weekend is good for me, for the reason that this time i am reading this enormous informative article here at my home.
Leave a comment
Recent tutorials
Polpular tutorials
Most commented tutorials
Categories
Purpose of this website
Educational robotics refers to the use of robots and robotics technology to promote learning in educational settings. It involves the integration of technology, engineering, and computer science into the classroom, allowing students to engage in hands-on, project-based learning experiences.
In this context, our website represents an excellent resource for parents, teachers and children who wish to discover robotics.
Contact details
Zaouiet Kontech-Jemmel-Monastir-Tunisia
Popular articles
Robotic site created by Mohamed Ali Haj Salah - Teacher info

























