Esp32 board and Gmail SMTP

Tutorial plan
1- Presentation of Gmail SMTP
2- How send an email using ESP32 and Gmail SMTP ?
3- Materials Needed
4- Component Wiring
5- Programming ESP32 using Micropyton
Presentation of Gmail SMTP
Gmail SMTP is a protocol used to send emails through Gmail's servers. SMTP, or Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, is the standard communication protocol for sending emails, and Gmail provides specific configurations to securely and efficiently use its email service in various applications or devices.
The primary purpose of Gmail SMTP is to enable third-party applications, services, or devices (like email clients, automation scripts, or IoT devices) to send emails through Gmail's servers. This is essential for use cases such as automated notifications, sending reports, or personal communication through custom applications.
Gmail SMTP is designed with strong security features:
1- SSL/TLS Encryption: Ensures all communication between your device and Gmail's servers is encrypted.
2- Authentication: Requires a valid Gmail username and password.
3- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): If enabled, an app-specific password must be used instead of the Gmail account password.
4- Spam Protection: Gmail's SMTP enforces rate limits and spam checks to prevent misuse.
How Gmail SMTP Works
1- Connection Initialization:
Your application or email client connects to Gmail's SMTP server using the appropriate port and encryption protocol.
2- Authentication:
The server verifies the provided username and password.
3- Email Composition:
Your application sends the email details (sender, recipient, subject, body, attachments) to the SMTP server.
4- Email Delivery:
Gmail's servers handle the delivery of the email to the recipient's mail server.
How send an email using ESP32 and Gmail SMTP ?
Sending an email using an ESP32, a push button, MicroPython, and Gmail SMTP involves combining GPIO handling for the button and SMTP communication for email sending.
How It Works
1- Wi-Fi Connection:
The ESP32 connects to the Wi-Fi network specified by SSID and PASSWORD.
2- SMTP Setup:
Gmail SMTP server is configured for sending emails.
3- Push Button Handling:
The GPIO pin connected to the button is monitored for a LOW state (button press).
4- Email Trigger:
When the button is pressed, an email is composed and sent via Gmail SMTP.
Materials Needed
ESP32:

The microcontroller that interfaces with the push button and connects to the internet.
Push Button:

When pressed, triggers the ESP32 to send an email.
Jumper Wires

Jumper wires will be used to make connections between the components.
Breadboard:

A breadboard can be used to create a temporary circuit for testing and prototyping.
Component Wiring
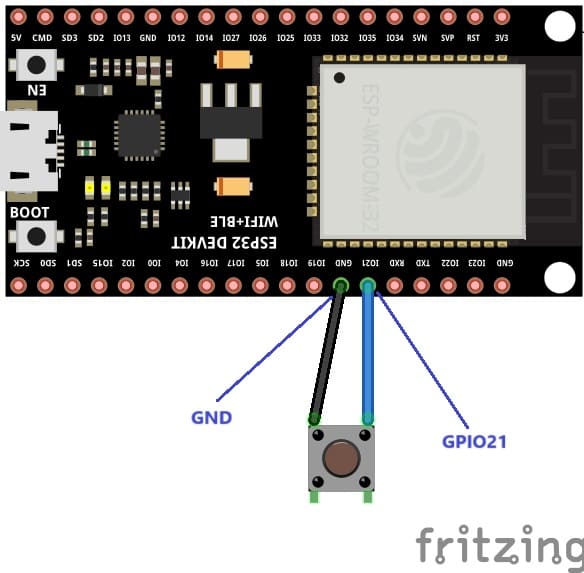
To perform the assembly, you can connect
1- the first tab of push button to GPIO21 of ESP32 board
2- the second leg of pushbutton to GND pin of ESP32 board
Programming ESP32 using Micropyton
you must import the two libraries: ConnectWifi.py and umail.py.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
from machine import Pin button = Pin(21, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP) import ConnectWifi ConnectWifi.connect() import umail while True: if not button.value(): #When we press the button smtp = umail.SMTP('smtp.gmail.com', 587, username='adresse-émtteur@gmail.com', password='*********') smtp.to('adresse_recepteur@gmail.com') smtp.send("Message sended by ESP32") smtp.quit() |