Using 28BYJ-48 stepper motor by ESP32
Tutorial plan
1- Definition of 28BYJ-48 stepper motor
2- Components Needed to command 28BYJ-48 stepper motor by ESP32
3- Circuit Setup
4- Programming the ESP32 with micropython
Definition of 28BYJ-48 stepper motor
The 28BYJ-48 is a small, inexpensive, unipolar stepper motor widely used in DIY electronics projects, automation, and hobby robotics due to its high precision and ease of use with microcontrollers like the Arduino. It operates through precise steps, making it ideal for applications requiring controlled movement, like in camera gimbals, robotic arms, and small CNC machines.
Key Characteristics
Type: Unipolar stepper motor.
Operating Voltage: Typically operates at 5V DC, which makes it compatible with standard USB power sources and microcontroller output.
Step Angle: It has a step angle of 5.625°, meaning it takes 64 steps to complete one rotation of the motor shaft.
Gear Ratio: The motor includes an internal gearbox with a gear reduction ratio of 1/64, which increases the precision of movement to 4096 steps per revolution of the output shaft (64 steps × 64 gear ratio = 4096 microsteps).
Torque: The gearbox increases torque, making the motor suitable for low-speed applications that require more force.
Control: Controlled by an external driver circuit, such as the ULN2003 driver board, which helps to sequence the power to the coils in the correct order to produce smooth movement.
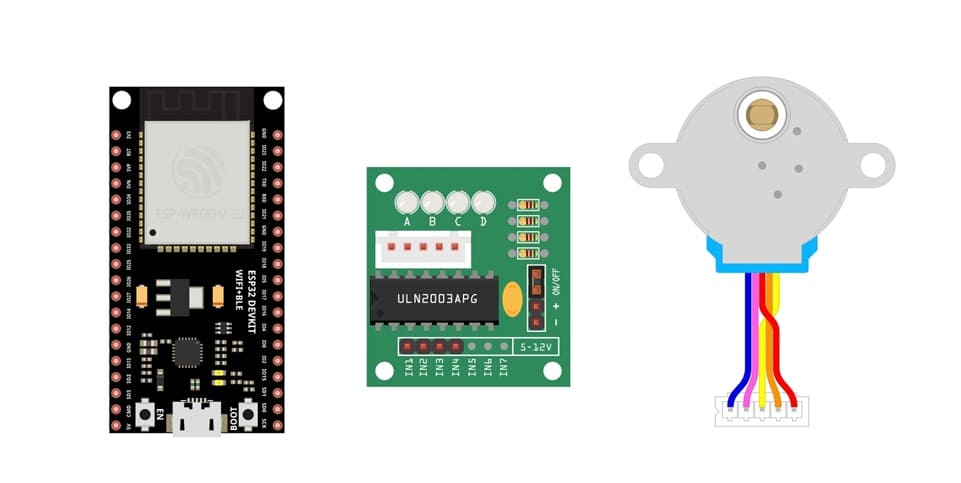
Components Needed to command 28BYJ-48 stepper motor by ESP32
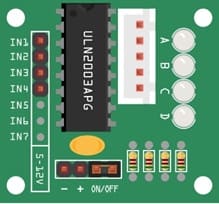
To control a 28BYJ-48 stepper motor with an ESP32, you’ll typically need a ULN2003 driver module. The ULN2003 helps to manage the current needed by the motor, which the ESP32 can’t handle directly due to its limited current output per GPIO pin. Here’s a guide to wiring and coding the setup.
ESP32 Microcontroller:
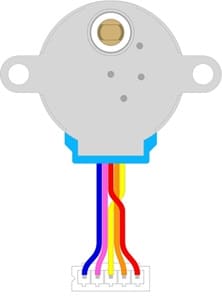
28BYJ-48 stepper motor
ULN2003 driver board for the stepper motor
Connecting Wires:

Breadboard (Optional):

Power Supply:
Circuit Setup
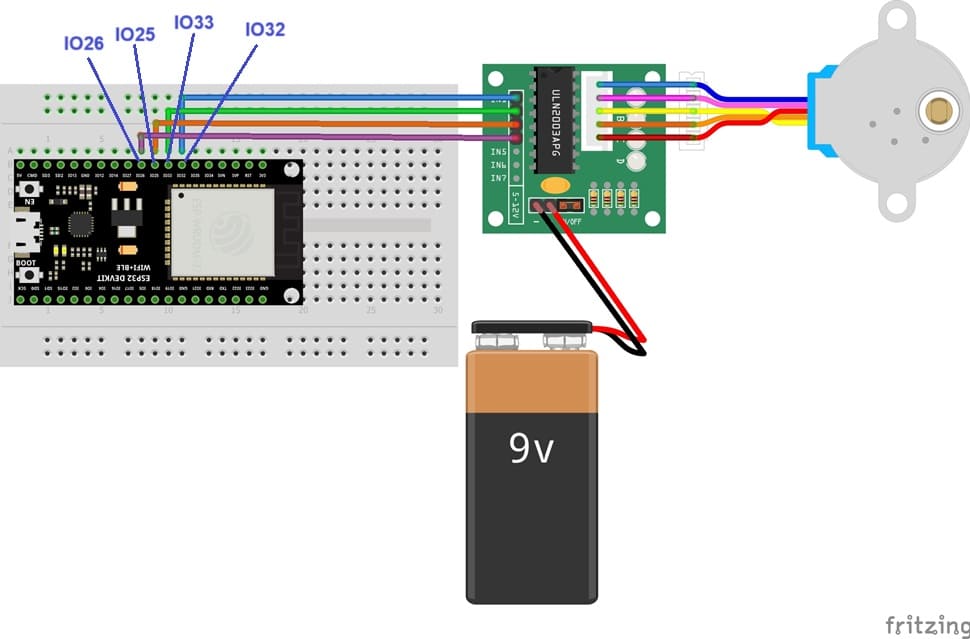
Connect the 28BYJ-48 to the ULN2003 driver module:
The 28BYJ-48 stepper motor typically has a 5-pin connector that fits directly into the ULN2003 board.
Connect the ULN2003 to the ESP32:
IN1 on ULN2003 → GPIO 32 on ESP32
IN2 on ULN2003 → GPIO 33 on ESP32
IN3 on ULN2003 → GPIO 25 on ESP32
IN4 on ULN2003 → GPIO 26 on ESP32
VCC on ULN2003 → (+) on power supply (9V battery)
GND on ULN2003 → (-) of power supply (9V battery)
Programming the ESP32 with micropython
You can use the Stepper library to simplify the control of the motor.
Here’s an example of code to control the 28BYJ-48 stepper motor: