Send data measured by DHT22 sensor connected to ESP32 via Bluetooth
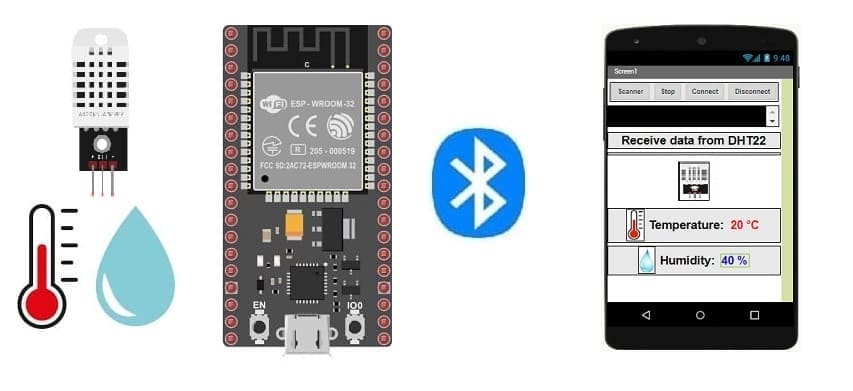
Tutorial plan
1- How to send temperature and humidity measured by DHT22 sensor to smartphone via Bluetooth ?
2- The components required to use DHT22 sensor by ESP32 board
3- Mounting the ESP32 board with the DHT22 sensor
4- Program the ESP32 board with Micropython
5- Develop a mobile application with App Inventor
How to send temperature and humidity measured by DHT22 sensor to smartphone via Bluetooth ?
To send temperature and humidity data measured by a DHT22 sensor to a smartphone via Bluetooth, you can follow these general steps using an ESP32 microcontroller:
Hardware Setup:
Connect the DHT22 sensor to the ESP32. Typically, it involves connecting three wires: one for 3.3V, one for GND, and one for data (signal).
Software Setup:
Install the necessary libraries for the DHT sensor and Bluetooth communication in the Micropython:
- For the DHT sensor, you can use the "DHT ".
- For Bluetooth communication, the ESP32 has a built-in BluetoothSerial library.
Smartphone Setup:
Use the available blocks in App Inventor to:
- establish a Bluetooth connection with the ESP32
- receive the data sent by the ESP32 via Bluetooth
- display it in your app.
Data Reception on Smartphone:
Pair your smartphone with the ESP32 using the Bluetooth settings. Once connected, the smartphone will receive the temperature and humidity data from the ESP32 over Bluetooth.
You can view and monitor the data in real-time through the terminal application on your smartphone.
The components required to use DHT22 sensor by ESP32 board
ESP32 board:
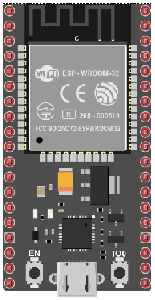
The ESP32 is a powerful microcontroller developed by Espressif Systems. It's renowned for its integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, making it a popular choice for various IoT (Internet of Things) applications.
DHT22 Temperature and Humidity Sensor

The DHT22 sensor, also known as AM2302, is a popular digital humidity and temperature sensor. It is commonly used in electronics projects and home automation for monitoring environmental conditions.
Jumper Wires:

For making temporary connections and wiring between components.
Breadboard:

A breadboard is a useful tool for creating temporary electronic circuits. It allows you to connect components without soldering.
Mounting the ESP32 board with the DHT22 sensor
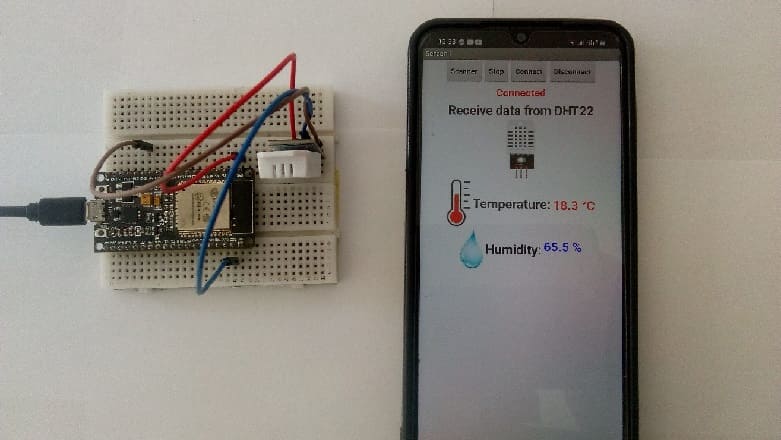
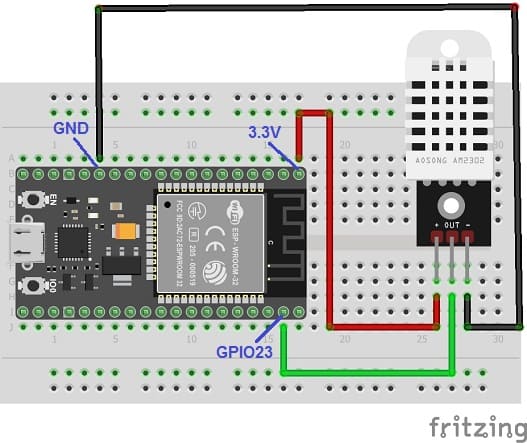

This represents the basic connections between the DHT22 sensor and the ESP32 board:
- Connect the VCC(+) pin of the DHT22 sensor to the 3.3V pin on the ESP32 board.
- Connect the OUT pin of the DHT22 sensor to a digital pin GPIO 23 on the ESP32 board.
- Connect the GND(-) pin of the DHT22 sensor to any ground (GND) pin on the ESP32 board.
Programming the ESP32 with MicroPython:
1- Flash your ESP32 with MicroPython using this file esp32-20210902-v1.17.bin.
2- import this two libraries : ble_uart_peripheral.py and ble_advertising.py
3- Writing MicroPython code for the DHT22 sensor:
Here's an example of MicroPython code to read data from the DHT22 sensor and send it via Bluetooth:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 |
########## DIGITAL MANUFACTURING ########## # PIKACHU Project # Authors: Miguel Angel Guzman # Kadriye Nur Bakirci ########################################### ########## IMPORT REQUIRED LIBRARIES ########## import bluetooth from ble_uart_peripheral import BLEUART from machine import Pin import dht import time # DHT22 sensor configuration p23=Pin(23, Pin.IN) d=dht.DHT22(p23) # Create BLE object ble = bluetooth.BLE() # Open UART session for BLE uart = BLEUART(ble) # Define ISR for an UART input on BLE connection def on_rx(): # Read UART string, AppInventor sends raw bytes uart_in = uart.read() # read the message received from the Smartphone via Bluetooth print("UART IN: ", uart_in.decode()) # display the message received from the Smartphone on the Thonny console # Map ISR to UART read interrupt def env_tx(val_tx): uart.write(str(val_tx) + '\n') print("tx", val_tx) # Map ISR to UART read interrupt uart.irq(handler=on_rx) while True: message=""; d.measure() # Read data from the DHT22 sensor t=d.temperature() # read temperature h=d.humidity() # read l'humidity print('Temperature=', t, 'C') print('Humidity=', h) message=str(t)+" °C" env_tx(message) # send temperature to Smartphone message=str(h)+" %" env_tx(message) # send humdity to Smartphone time.sleep_ms(2000) uart.close() |
Develop a mobile application with App Inventor
1- Create the designer of mobile app with App Inventor.
- Use the available Bluetooth components to establish a connection with the ESP32.
- Add labels or text fields to display the received sensor data.
Here is the Designer part of the application with App Inventor :
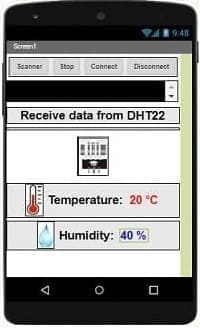
2. Programming the application with App Inventor:
a- Use the available blocks in App Inventor to establish a Bluetooth connection with the ESP32.
- Starting with Android 12, Bluetooth permissions have been enhanced to improve security and user data protection. This is why we must declare the authorizations that your application needs in the AndroidManifest.xml file. For Bluetooth, you'll need to include ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION, BLUETOOTH_SCAN, and possibly BLUETOOTH_CONNECT permissions, depending on the features you're using.
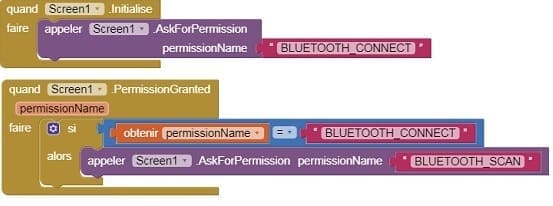
- Use these programming blocks to connect the smartphone to the ESP32 board via Bluetooth:
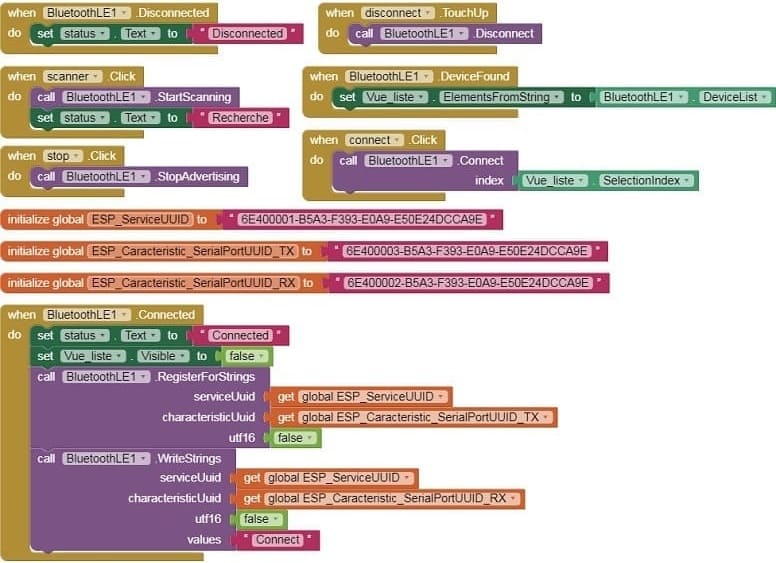
b- Receive the data sent by the ESP32 via Bluetooth and display it in your app.
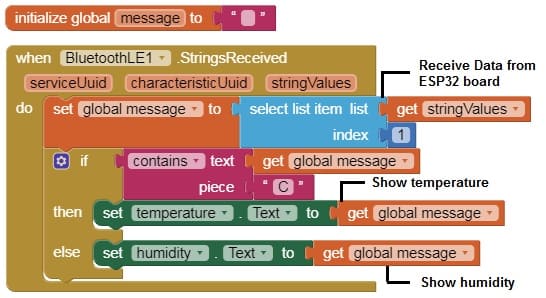
Download project Download application
Testing and Debugging:
1- Upload the MicroPython code to your ESP32.
2- Install and launch the app created with App Inventor on your smartphone.
3- Connect to the ESP32 from the app.
4- Verify that the temperature and humidity data from the DHT22 sensor are received and displayed correctly in the app.
























